pscplaton
- 5
- 1
Hello !
In the book Quantum Field for mathematician, there is this Wick diagram as an example to understand how to compute the symmetry factor (I am sorry, I draw it with paint...)
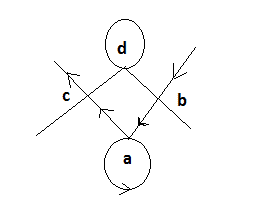
This is about a hermitian field interacting with a complex field. The book says it has a symmetry factor of 2 but I don't understand why, even after reading about symmetry factor on wikipedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feynman_diagram#Symmetry_factors). I don't see what are the two automorphisms of this Feynman diagram... As far as I understand, for a given automorphism, "a" can only be mapped to "a" because of the complex field loop, and the same applies for "d". "c" cannot be mapped to "b" because it has incoming complex propagator from "a", which is not the case of "b"...
Where am I wrong ?
Thanks!
In the book Quantum Field for mathematician, there is this Wick diagram as an example to understand how to compute the symmetry factor (I am sorry, I draw it with paint...)
This is about a hermitian field interacting with a complex field. The book says it has a symmetry factor of 2 but I don't understand why, even after reading about symmetry factor on wikipedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feynman_diagram#Symmetry_factors). I don't see what are the two automorphisms of this Feynman diagram... As far as I understand, for a given automorphism, "a" can only be mapped to "a" because of the complex field loop, and the same applies for "d". "c" cannot be mapped to "b" because it has incoming complex propagator from "a", which is not the case of "b"...
Where am I wrong ?
Thanks!