- #1
gangsterlover
- 31
- 0
Hi,
Take a look at this synthesis of aspirin. Because I am noob, please bare with me.
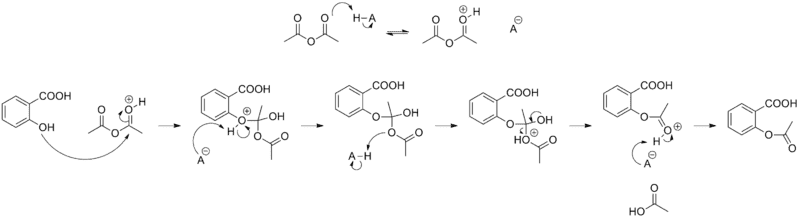
On the top there you can see how the acetic anhydride gets attacked by the H plus ion.
I can't understand why the h plus ion gets bonded there.
I`ve been trying to find the answer to this question for quite some time now, and this is what I have come up to.
1. There is no charge on none of the oxygen atoms. So not explanation there.
2. There is no difference in electronegativity between the oxygen as far as I can see, but please tell me different. I would actually not mind, because I am totally stuck.
3. There was this one step on(http://www.masterorganicchemistry.com/2012/06/18/what-makes-a-good-nucleophile/) which said something about solvent, but I didn`t understand it too well, so I`ll just move on to steric hindrance.
4. Steric hindrance could explain why the h plus ion doesn`t bond at the bottom oxygen on the acetic anhydride, but not why the h plus ion doesn`t want to bond on the salicylic acid oxygen in the top left corner.
Omg...
yelp!
Take a look at this synthesis of aspirin. Because I am noob, please bare with me.
On the top there you can see how the acetic anhydride gets attacked by the H plus ion.
I can't understand why the h plus ion gets bonded there.
I`ve been trying to find the answer to this question for quite some time now, and this is what I have come up to.
1. There is no charge on none of the oxygen atoms. So not explanation there.
2. There is no difference in electronegativity between the oxygen as far as I can see, but please tell me different. I would actually not mind, because I am totally stuck.
3. There was this one step on(http://www.masterorganicchemistry.com/2012/06/18/what-makes-a-good-nucleophile/) which said something about solvent, but I didn`t understand it too well, so I`ll just move on to steric hindrance.
4. Steric hindrance could explain why the h plus ion doesn`t bond at the bottom oxygen on the acetic anhydride, but not why the h plus ion doesn`t want to bond on the salicylic acid oxygen in the top left corner.
Omg...
yelp!