Vivianian
- 3
- 0
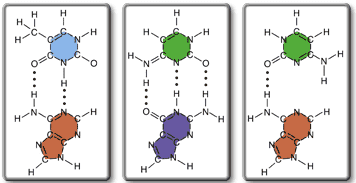
Rank the following base pairs according to their stability.
Rank from most to least stable. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
-------------
I have found out that the first one is thymine-adenine pair and the second one is a cytosine-guanine pair. The third one is cytosine paired with adenine, which doesn't make sense, so it must be the least stable. Now how do I go about determining if the A-T pair or C-G pair is more stable? It has something to do with the number of bonds, maybe?
Rank from most to least stable. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
-------------
I have found out that the first one is thymine-adenine pair and the second one is a cytosine-guanine pair. The third one is cytosine paired with adenine, which doesn't make sense, so it must be the least stable. Now how do I go about determining if the A-T pair or C-G pair is more stable? It has something to do with the number of bonds, maybe?