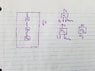
SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on calculating the net force on the middle mass (m2=9.6 kg) in an elevator accelerating downwards at -2.5 m/s². The correct approach involves using the equation F=ma, resulting in a net force of 24 N acting upwards on the middle mass. The initial attempts to calculate the force neglected the spring's contribution, which was clarified later in the discussion. A diagram and free body diagrams (FBD) were suggested for better understanding.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Newton's Second Law (F=ma)
- Knowledge of spring force calculations (Force(spring)=-kx)
- Familiarity with free body diagrams (FBD) for visualizing forces
- Basic concepts of mass and acceleration in physics
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of free body diagrams (FBD) in physics
- Learn about spring constants and their applications in mechanics
- Explore the effects of acceleration on forces in non-inertial reference frames
- Review examples of net force calculations in multi-mass systems
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and forces in dynamic systems, as well as educators looking for examples of problem-solving in force calculations.