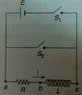
SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the time constant of an inductor coil when shorted in a circuit. The time constant, denoted as t_c, is defined as t_c = L/R, where L is the inductance and R is the resistance. When the inductor is shorted, the potential difference across the coil becomes zero, as the entire induced EMF drops across the internal resistance of the coil. The current through the battery remains constant, while the current through the inductor decays exponentially over time.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of inductance and resistance in electrical circuits
- Familiarity with the differential equation
L (dI/dt) + IR = 0
- Knowledge of the exponential decay function
I(t) = I_o e^{-R t/L}
- Basic concepts of DC circuits and short-circuiting components
NEXT STEPS
- Study the behavior of inductors in RL circuits under various conditions
- Learn about the implications of short-circuiting inductors in practical applications
- Explore the concept of back EMF and its effects on circuit components
- Investigate the role of internal resistance in inductors and its impact on circuit performance
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone interested in understanding the dynamics of inductors in electrical circuits.