Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the design and functionality of a self-constructed telephoto lens system intended for imaging a cantilever with specific dimensions. Participants explore the relationship between focal lengths and magnification, as well as the implications for working distance in the lens setup.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
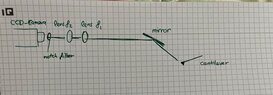
- One participant describes a telephoto lens system consisting of two lenses, noting that the image magnification is determined by the ratio of their focal lengths.
- Another participant requests clarification on the setup, questioning the definition of "the cantilever" and suggesting the need for an annotated diagram.
- A participant reiterates the question of whether total focal length matters when using different lens combinations that yield the same magnification.
- Further inquiries are made about the use of the lensmaker's equation to calculate working distance, specifically which focal length should be used in the equation.
- Another participant comments on the use of a telescope rather than a microscope, emphasizing the need for a larger objective lens to maximize light collection while addressing potential distortion issues.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the relevance of total focal length in relation to magnification and the appropriate setup for imaging. There is no consensus on the best approach to calculating working distance or the suitability of using a telescope versus a microscope.
Contextual Notes
Participants have not resolved the assumptions regarding object distance and the applicability of the telescope formula. There are also uncertainties about the specific definitions and parameters involved in the lens system.