SUMMARY
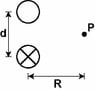
The discussion centers on calculating the magnetic field intensity at a point equidistant from two parallel wires carrying equal anti-parallel currents of 1.80 A, separated by a distance of 1.50 cm. The magnetic field intensity formula used is B = (μ₀I)/(2πr) for an infinite wire. Participants clarify that the magnetic fields from the two wires do not cancel out at the midpoint, contrary to initial assumptions, and emphasize the importance of vector analysis in determining the resultant magnetic field. The correct approach involves recognizing that the magnetic fields add up rather than cancel when the currents are anti-parallel.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of magnetic field calculations using the formula B = (μ₀I)/(2πr).
- Familiarity with vector addition and cancellation in physics.
- Knowledge of the concept of anti-parallel currents in electromagnetism.
- Basic grasp of the geometry involved in magnetic field problems.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the implications of vector fields in electromagnetism, focusing on magnetic field interactions.
- Learn about the Biot-Savart Law and its application in calculating magnetic fields from current-carrying wires.
- Explore the concept of magnetic field lines and their behavior around parallel currents.
- Review problem-solving strategies for electromagnetism homework, particularly in vector analysis.
USEFUL FOR
Students studying electromagnetism, physics educators, and anyone involved in solving problems related to magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors.