SUMMARY
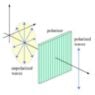
The discussion focuses on the nature of unpolarised light and its relationship with polarisation. Participants clarify that unpolarised light consists of multiple light waves with varying polarisation directions, all perpendicular to the direction of propagation. The conversation emphasizes the importance of the electric field (E-field) vector in understanding how light interacts with polarising filters, specifically using the cosine squared law to determine transmitted intensity. The resolution of polarised light into components along perpendicular axes is also discussed, highlighting the mathematical relationships involved.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of light wave propagation and polarisation
- Familiarity with E-field vectors and their significance in optics
- Knowledge of trigonometric functions, particularly cosine and sine
- Basic grasp of intensity calculations in wave physics
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of light polarisation and its applications in optics
- Learn about the mathematical derivation of the cosine squared law in polarisation
- Explore the quantum mechanics of light and photon behaviour in polarised states
- Investigate practical applications of polarisation in technologies such as LCD screens and photography
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, optical engineers, and anyone interested in the principles of light behaviour and polarisation techniques.