matangi7
- 7
- 0
My Textbook states"The same principle behind Faraday’s ice pail experiment is used in a Van de Graaff electrostatic generator (Fig. 22.26). A charged belt continuously carries charge to the inside of a conducting shell. By Gauss’s law, there can never be any charge on the inner surface of this shell, so the charge is immediately carried away to the outside surface of the shell."
How is Gauss's law relevant to the Van De Graaf Generator? Doesn't the situation have to be electrostatic to apply Gauss's law? Doesn't a Van De Graaf Machine have a current flowing, not static charges? Attached is the diagram in my textbook.
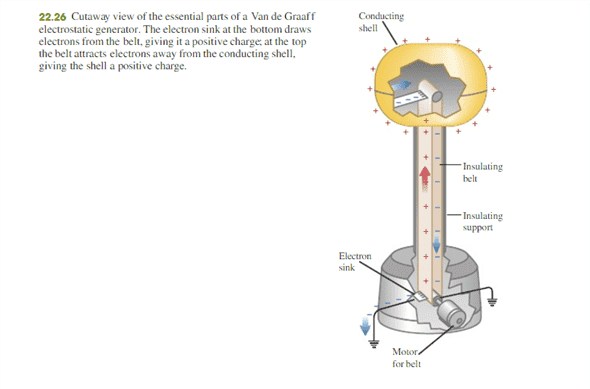
How is Gauss's law relevant to the Van De Graaf Generator? Doesn't the situation have to be electrostatic to apply Gauss's law? Doesn't a Van De Graaf Machine have a current flowing, not static charges? Attached is the diagram in my textbook.
