- #1
slakedlime
- 76
- 2
[SOLVED] Vectors: air speed, ground speed
I'm having trouble drawing the diagram for this question.
An airplane with air speed 120 km/h is heading due north in a wind blowing due east at 50 km/h. What is the ground speed of the plane?
Pythagoras theorem.
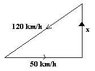
I've attached my version of the diagram with this message. I used the Pythagoras theorem since the wind blowing due east and the plane headed north meet at 90 degrees.
ground speed = sq. root {(120^2 + 50^2)}
= 130 km/h
The answer is supposed to be 60 km/h. Can someone please help or tell me where I went wrong? Thank you!
I'm having trouble drawing the diagram for this question.
Homework Statement
An airplane with air speed 120 km/h is heading due north in a wind blowing due east at 50 km/h. What is the ground speed of the plane?
Homework Equations
Pythagoras theorem.
The Attempt at a Solution
I've attached my version of the diagram with this message. I used the Pythagoras theorem since the wind blowing due east and the plane headed north meet at 90 degrees.
ground speed = sq. root {(120^2 + 50^2)}
= 130 km/h
The answer is supposed to be 60 km/h. Can someone please help or tell me where I went wrong? Thank you!
Attachments
Last edited: