SUMMARY
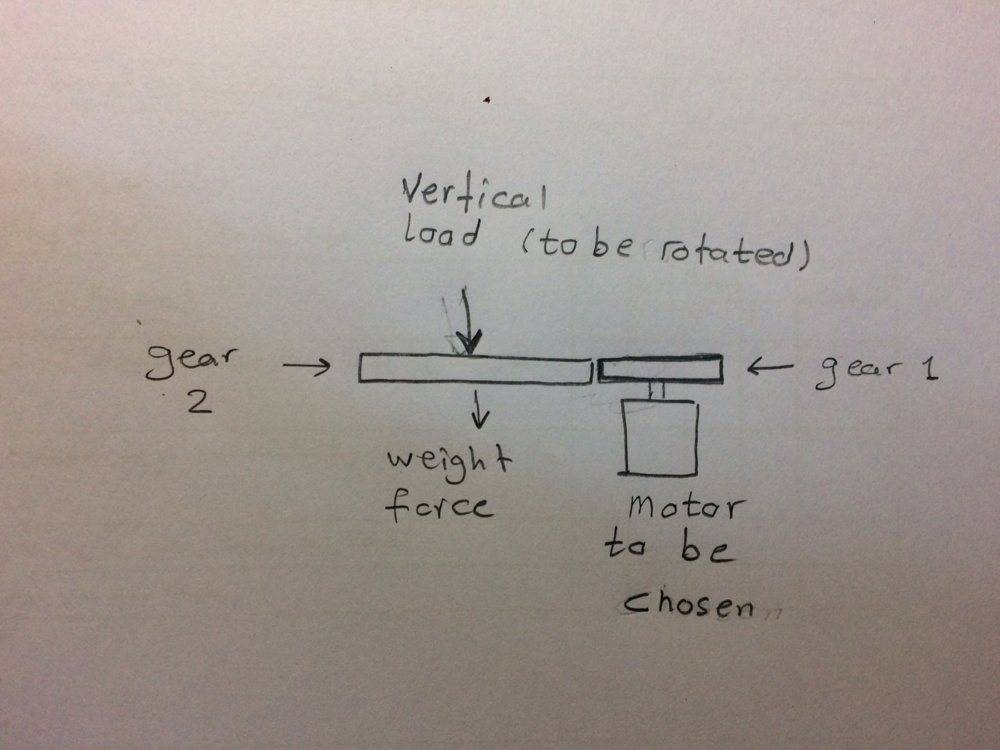
The discussion focuses on selecting the appropriate motor for a vertical load torque application, specifically for a solar tracker. Key formulas include Torque = mL, where m is mass and L is the distance from the center of gravity to the center of rotation. The torque required to rotate gear 2 is influenced by factors such as frictional forces, moment of inertia, and wind loads. Proper design considerations include using thrust bearings to support vertical loads and ensuring the motor can overcome friction and maintain constant speed.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of torque calculations, specifically Torque = mL
- Knowledge of bearing types, particularly thrust bearings and their applications
- Familiarity with gear mechanics and the implications of gear meshing
- Basic principles of environmental impacts on mechanical systems, such as wind load considerations
NEXT STEPS
- Research the calculation of torque required for vertical loads in mechanical systems
- Learn about thrust bearings and their role in supporting vertical shafts
- Investigate the effects of wind loads on solar tracker designs and how to calculate them
- Explore gear design principles, including the use of roller chains versus meshed gears
USEFUL FOR
Mechanical engineers, robotics designers, and anyone involved in the design and implementation of solar tracking systems or similar applications requiring precise motor torque calculations.