SUMMARY
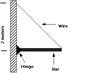
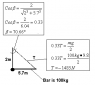
The discussion focuses on calculating the hinge force acting on a 3.4-meter-long beam with a mass of 100 kg. Participants emphasize the importance of using Newton's first law to resolve the forces acting on the beam, specifically the tension force (T) and its components in both the x and y directions. The correct approach involves drawing a free body diagram and applying the equations of equilibrium to find the resultant hinge force. Key calculations include determining T and resolving it into its components, leading to the conclusion that the hinge force can be derived from these components.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Newton's first law of motion
- Ability to draw and interpret free body diagrams
- Knowledge of trigonometric functions (sine and cosine)
- Familiarity with the equations of equilibrium for static systems
NEXT STEPS
- Learn how to draw and analyze free body diagrams for static equilibrium problems
- Study the application of Newton's laws in two-dimensional force systems
- Explore the concept of torque and its role in static equilibrium
- Practice solving similar problems involving tension and hinge forces in beams
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, engineering students, and anyone studying mechanics, particularly those focusing on static equilibrium and force analysis in structures.