SUMMARY
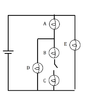
When the switch is closed in a circuit with bulbs A, D, B, and C, the brightness of each bulb changes due to variations in current and resistance. Bulb D, which is in parallel with bulbs B and C, experiences a decrease in brightness because the total current is split among them, while bulbs A and E maintain their brightness. The equivalent resistance of the circuit decreases, leading to an increase in total current, but the distribution of current results in bulb D dimming. The power dissipated in each bulb, which determines brightness, is directly related to the current flowing through it.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electric circuits and components
- Knowledge of Ohm's Law (V = I * R)
- Familiarity with series and parallel resistor configurations
- Ability to calculate equivalent resistance in parallel circuits
NEXT STEPS
- Learn how to calculate equivalent resistance in complex circuits
- Study the principles of current division in parallel circuits
- Explore the relationship between power, current, and brightness in electrical components
- Investigate the effects of changing resistance on current flow in series and parallel circuits
USEFUL FOR
Students studying electrical engineering, educators teaching circuit theory, and hobbyists working on electronics projects involving light bulbs and resistors.