SUMMARY
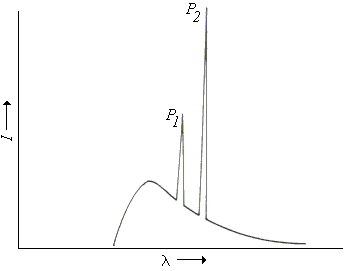
The Bremsstrahlung X-ray spectrum is characterized by a continuous distribution of X-ray energies resulting from the deceleration of charged particles, primarily electrons, when they interact with matter. The function that describes the shape of this spectrum curve, excluding characteristic spikes, is typically represented by the equation derived from quantum electrodynamics principles. This equation effectively models the intensity of emitted X-rays as a function of energy, providing insights into the underlying physics of X-ray production.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of quantum electrodynamics principles
- Familiarity with X-ray production mechanisms
- Basic knowledge of spectrum analysis
- Mathematical proficiency in interpreting equations
NEXT STEPS
- Research the mathematical derivation of the Bremsstrahlung spectrum equation
- Explore the role of electron acceleration in X-ray production
- Study the impact of material composition on the Bremsstrahlung spectrum
- Learn about experimental methods for measuring X-ray spectra
USEFUL FOR
Physicists, radiologists, and researchers in materials science who are studying X-ray production and its applications in various fields.