- 19,865
- 10,851
<br /> <br /> <a href="https://www.physicsforums.com/insights/what-is-the-double-slit-a-5-minute-introduction/" class="link link--internal">Continue reading...</a>Definition/Summary
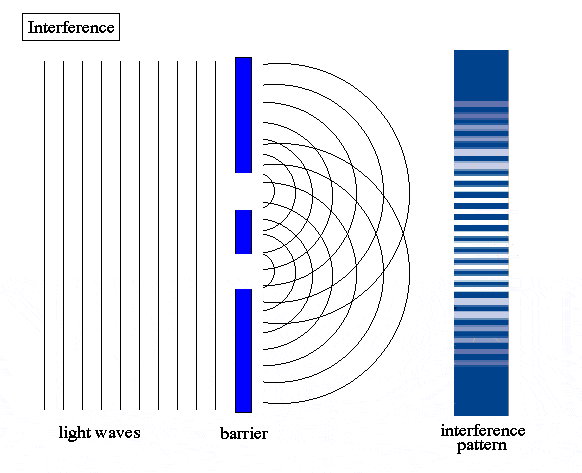
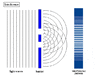
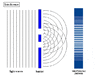
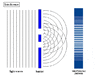
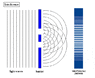
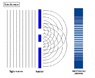
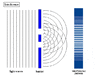
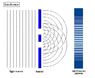
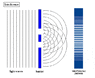
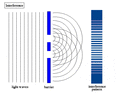
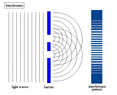
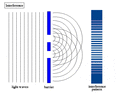
The double-slit is a simple configuration used to demonstrate interference effects in waves.
Equations
At distances that are large compared to the spacing between the slits (i.e. the far-field), the interference maxima (bright fringes) occur at angles such that
d \ \sin\theta \ = \ m \ \lambda
where
\begin{align*}d & = \text{the slit spacing (center-to-center)} \\\theta & = \text{the far-field angle} \\m & = \text{(any integer) the order of the }m^{th} \text{ fringe} \\\lambda & = \text{wavelength}\end{align*}
and the minima (dark fringes, or zeroes) occur at
d \ \sin\theta \ = \ \left(m+\frac{1}{2}\right) \ \lambda
The far-field intensity, as a function of angle, is given by
I(\theta) \ = \ 4 I_0 \cdot\cos^2 \delta \cdot\left( \frac{\sin \beta}{\beta} \right)^2
where
\begin{align*}I_0 & = \text{Central peak intensity due...
Attachments
-
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 200
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 200 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 176
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 176 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 175
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 175 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 157
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 157 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 145
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 145 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 150
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 150 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 144
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 144 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 150
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 150 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 144
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 144 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 137
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 137 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 157
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 157 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 155
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 155 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 132
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 132 -
 interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 129
interference.gif9.6 KB · Views: 129
Last edited: