What is the Negative of a Polar Coordinate?
- Context: High School
- Thread starter Physicist3
- Start date
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
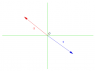
The negative of a polar coordinate is determined by inverting the angle by 180 degrees while maintaining the same magnitude. For the polar value 10@-75°, the additive inverse, denoted as -x, is represented as 10@105°. This follows the principle that in polar coordinates, the negative of a vector has the same magnitude but an angle that differs by 180 degrees. Understanding this concept is crucial for accurate vector representation in polar coordinates.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of polar coordinates and their representation
- Familiarity with vector addition in Euclidean geometry
- Knowledge of angle measurement and conversion
- Basic concepts of additive inverses in mathematics
- Study the principles of vector addition in polar coordinates
- Learn about the geometric interpretation of polar coordinates
- Explore the relationship between polar and Cartesian coordinates
- Investigate applications of polar coordinates in physics and engineering
Mathematicians, physics students, engineers, and anyone working with vector analysis and polar coordinates will benefit from this discussion.
Similar threads
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 7 ·
- · Replies 14 ·
- · Replies 4 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 7 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 5 ·
- · Replies 3 ·