logearav
- 329
- 0
friends,
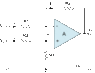
what is the role of potential or voltage divider in a circuit? in an operational amplifier circuit, while applying inputs to non inverting input, when two resistances are connected are connected across the battery they said to form a voltage divider. if the first resistance is r3 and second one is r4 which is grounded, the equivalent equation is r4/(r3+r4). what is the theory involved in voltage divider and current divider? also what is the theory behind this equation. help in this regard will be greatly appreciated. please refer my attachment provided
what is the role of potential or voltage divider in a circuit? in an operational amplifier circuit, while applying inputs to non inverting input, when two resistances are connected are connected across the battery they said to form a voltage divider. if the first resistance is r3 and second one is r4 which is grounded, the equivalent equation is r4/(r3+r4). what is the theory involved in voltage divider and current divider? also what is the theory behind this equation. help in this regard will be greatly appreciated. please refer my attachment provided
Attachments
Last edited: