Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around estimating the equivalent capacitance of a typical car battery, exploring the similarities and differences between batteries and capacitors. Participants engage in a theoretical exploration of charge storage mechanisms, discharge characteristics, and the implications of comparing these two types of electrical components.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Debate/contested
- Technical explanation
Main Points Raised
- One participant estimates the equivalent capacitance of a fully charged car battery to be around 500F, while another calculates it to be approximately 15,000F at maximum charge.
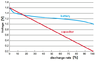
- Some participants emphasize that a battery and a capacitor have different discharge characteristics, with one noting that comparisons may not be meaningful.
- Another participant highlights that while a battery is a DC source with zero frequency, a capacitor's reactance is frequency-dependent, leading to infinite resistance at zero frequency.
- There is mention of the Earth having a capacitance of around 70μF, with another participant suggesting it is closer to 700μF.
- One participant introduces a model from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory that simulates a battery as a combination of capacitors and resistors, suggesting that the relationship between charge and voltage in batteries is non-linear.
- Several participants acknowledge the similarities between batteries and capacitors, noting that both can charge each other despite their differences.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the validity of comparing batteries to capacitors, with some arguing against the comparison while others highlight the similarities. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the appropriateness of such comparisons and the implications of the estimated capacitance values.
Contextual Notes
Participants note that the discharge characteristics of batteries and capacitors differ significantly, and the calculations for equivalent capacitance depend on various assumptions and conditions. The discussion also touches on the complexities of modeling batteries, indicating that a simple equivalent capacitance may not capture the full behavior of a battery.