SUMMARY
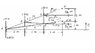
The discussion centers on understanding the calculation of distances in a truss problem, specifically the vertical distances from support points to nodes E and D. The correct vertical distance from the support to E is derived using proportions, resulting in 2/3 m, while the distance from E to D is confirmed as 1 m. The participant expresses a need for resources to refresh their knowledge in algebra and trigonometry to better tackle physics problems, particularly in Statics. Recommendations include online resources like Wikipedia math articles and Paul's Online Math Notes for foundational concepts.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic algebra and trigonometry concepts
- Familiarity with proportions and their applications in problem-solving
- Knowledge of Statics principles
- Ability to interpret and analyze geometric relationships in physics problems
NEXT STEPS
- Explore online resources for algebra and trigonometry refreshers, such as Paul's Online Math Notes
- Study geometry principles relevant to Statics problems
- Practice solving truss problems using proportional reasoning
- Review physics textbooks that cover Statics and its mathematical foundations
USEFUL FOR
Students returning to academic study, particularly those in engineering or physics courses, as well as anyone seeking to strengthen their foundational math skills for problem-solving in Statics.