- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Wormole and reactionless drive
- Thread starter Edi
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Drive
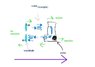
In summary, the picture attached and the title of the topic should explain the idea. There is a picture attached with a title of topic that explains the idea. The picture is not supposed to be understood by the viewer. The picture is of a water droplet coming out of a wormhole. The water droplet comes out of the wormhole because of inertia. What is causing the water to come out of the wormhole? What happens as your "ship" moves away from the wormhole?
Physics news on Phys.org
- #2
russ_watters
Mentor
- 23,163
- 10,373
I can't make any sense of that pic.
- #3
HallsofIvy
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 42,989
- 975
Do you have two wormholes with something (water?) going in one end and out the other or is that two ends of the same wormhole? What is causing the water to come out of the wormhole? What happens as your "ship" moves away from the wormhole?
- #4
Edi
- 177
- 1
Well, it is supposed to be one wormhole with both ends in the "ship". Watter, for example, is pumped in the lower hole and it comes out the upper, other end of the hole. What causes it to come out? Inertia (spell?)?
When the pump pushes watter out of it self it recoils back, but the watters kinetic energy isn't absorbed by the back of the "ship", but instead comes out the other end of the wormhole and is absorbed by the front of the "ship".
Now, this can't really be, because it violates some laws and would make "reaction-less drive" possible. What I want to know is where is this wrong, so no laws are broken. (?)
And the wormhole is supposed to be ON/IN the "ship".
When the pump pushes watter out of it self it recoils back, but the watters kinetic energy isn't absorbed by the back of the "ship", but instead comes out the other end of the wormhole and is absorbed by the front of the "ship".
Now, this can't really be, because it violates some laws and would make "reaction-less drive" possible. What I want to know is where is this wrong, so no laws are broken. (?)
And the wormhole is supposed to be ON/IN the "ship".
- #5
Vanadium 50
Staff Emeritus
Science Advisor
Education Advisor
2023 Award
- 33,277
- 19,799
"Please help me with my perpetual motion machine" is not something that this forum is well suited for - even if the help is trying to understand where it's wrong. There's a reason why perpetual motion machine threads seem to get locked quickly.
You've postulated a quasi-magical pair of disks where something going into one with momentum p comes out of the other with momentum -p, all without changing the disks' momentum. Why are you surprised that this doesn't conserve momentum?
You've postulated a quasi-magical pair of disks where something going into one with momentum p comes out of the other with momentum -p, all without changing the disks' momentum. Why are you surprised that this doesn't conserve momentum?
- #6
Edi
- 177
- 1
Because its a wormhole - you don't hit anything when going in one, you don't touch anything. Just go through it without losing momentum. If one loses momentum, where does it go?
I'm not saying this is true, just want to know what and how.
I'm not saying this is true, just want to know what and how.
- #7
m.starkov
- 35
- 0
I guess all you have to understand is that such holes can't exist w/o massive object.
But if you will get one (massive object) then all momentum will come to it :)
But if you will get one (massive object) then all momentum will come to it :)
- #8
Vanadium 50
Staff Emeritus
Science Advisor
Education Advisor
2023 Award
- 33,277
- 19,799
Edi said:Because its a wormhole
Because it's a fribbitz.
Because it's a globschnurz.
You can always postulate something with unphysical properties and give it a name. That doesn't make its properties any more physical.
- #9
Phrak
- 4,267
- 6
Edi said:Because its a wormhole - you don't hit anything when going in one, you don't touch anything. Just go through it without losing momentum. If one loses momentum, where does it go?
I'm not saying this is true, just want to know what and how.
How old are you, Edi?
These GENTLEMEN might be more inclined to help, if you had a better drawing. I can't understand it, myself.
- #10
HallsofIvy
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 42,989
- 975
Aww, c'mon. Who are you calling a GENTLEMAN!
- #11
Phrak
- 4,267
- 6
HallsofIvy said:Aww, c'mon. Who are you calling a GENTLEMAN!
Sorry. I was overreacting.
- #12
Edi
- 177
- 1
Ok, so its a fast sketch. I understand it :tongue:
17 btw.
A large wormhole might need a lot of mass/ energy, but how about i micro one? Subatomic level. And the water is not water, but a photon, for example.
The mass... the mass... that rises another question. To create a wormhole one would need to put a lot of energy/ mass in small enough space, but where does that energy go? Does the "mouth" of a wormhole have mass?
17 btw.
A large wormhole might need a lot of mass/ energy, but how about i micro one? Subatomic level. And the water is not water, but a photon, for example.
The mass... the mass... that rises another question. To create a wormhole one would need to put a lot of energy/ mass in small enough space, but where does that energy go? Does the "mouth" of a wormhole have mass?
Last edited:
- #13
Relay
- 56
- 0
I've never seen a real wormhole like the one everbody is talking about here. The only wormholes I've seen was when I was worm picking oh so many years ago. It wasn't a bad job, it paid well for the time. Anyhow, has anybody actually seen a real life step in here and step out on Mars type of wormhole. What are the chances of a wormhole forming at the center of the sun and the other end in Florida someplace. I could never wrap my brain around this concept.
- #14
- 10,302
- 1,472
Wormholes have not actually been observed, but are - not exactly a prediction, but rather perhaps a distant possibility, according to General Relativity. For instance, the Moris-Thorne wormhole.
They are of enough theoretical interest to have inspired numerous scientfic papers which investiage their predicted properties.
Of course, those sorts of wormholes that are predicted as possible by GR conserve momentum when they are in a closed system, though they do have other strange properties.
I suppose I should add that the property of conserving momentum implies that the space-drive discussed by the original poster wouldn't work, in case it isn't obvious.
They are of enough theoretical interest to have inspired numerous scientfic papers which investiage their predicted properties.
Of course, those sorts of wormholes that are predicted as possible by GR conserve momentum when they are in a closed system, though they do have other strange properties.
I suppose I should add that the property of conserving momentum implies that the space-drive discussed by the original poster wouldn't work, in case it isn't obvious.
- #15
JesseM
Science Advisor
- 8,520
- 16
I remember pervect had an interesting post about wormholes and energy conservation in post #6 of this thread...
- #16
- 10,302
- 1,472
Some scenarios involving wormholes have one of the mouths acquiring negative mass, since when an object (possibly just interstellar gas) exits a wormhole, that end of the wormhole mouth loses mass (ADM mass).
This gets weird quickly. I haven't seen any good theoretical resolution to this issue. Personally I find it hard to believe that negative mass exists, and no such thing has actually been observed.
I'm not really sure if anyone has looked for negative mass wormhole mouths in any of the large number of gravitational lensing studies that have been done - though I know there was either a paper or a letter that was written about the issue by Cramer, Benford, et al.
This gets weird quickly. I haven't seen any good theoretical resolution to this issue. Personally I find it hard to believe that negative mass exists, and no such thing has actually been observed.
I'm not really sure if anyone has looked for negative mass wormhole mouths in any of the large number of gravitational lensing studies that have been done - though I know there was either a paper or a letter that was written about the issue by Cramer, Benford, et al.
Last edited:
1. What is a wormhole and how does it work?
A wormhole is a hypothetical tunnel-like structure in space-time that connects two distant points. It is theorized to be able to bend space-time, allowing for travel between two points that would otherwise be impossible to reach in a reasonable amount of time. The exact mechanism of how a wormhole would work is still a topic of debate among scientists.
2. Can wormholes be used for faster-than-light travel?
While wormholes are theoretically capable of allowing for faster-than-light travel, the current understanding of physics suggests that it would require the existence of exotic matter with negative energy density, which has not been observed. Therefore, the use of wormholes for faster-than-light travel is still considered highly speculative.
3. What is a reactionless drive and how does it differ from traditional propulsion systems?
A reactionless drive is a propulsion system that does not rely on the principle of action and reaction, as traditional propulsion systems do. Instead, it uses a different mechanism, such as manipulating the fabric of space-time, to generate thrust without the need for any propellant. This would allow for travel without the limitations of traditional propulsion, such as the need for refueling.
4. Is the concept of a reactionless drive scientifically valid?
The concept of a reactionless drive is still a topic of debate and has not been proven to be scientifically valid. While there have been some theoretical proposals and experimental attempts to create reactionless drives, there is currently no evidence that they are possible based on our current understanding of physics.
5. Are there any potential applications for wormholes and reactionless drives?
If wormholes and reactionless drives were to be proven scientifically valid and able to be created and controlled, they could potentially have numerous applications in space exploration and travel. These could include faster travel to distant planets, exploration of other galaxies, and even the possibility of time travel. However, much more research and development would be needed before these applications could become a reality.
Similar threads
-
Special and General Relativity
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 604
-
Special and General Relativity
- Replies
- 15
- Views
- 1K
-
Special and General Relativity
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 1K
-
Special and General Relativity
- Replies
- 13
- Views
- 1K
-
Special and General Relativity
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 791
-
Special and General Relativity
- Replies
- 13
- Views
- 1K
-
Special and General Relativity
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 2K
-
Special and General Relativity
- Replies
- 11
- Views
- 991
-
Special and General Relativity
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 493
-
DIY Projects
- Replies
- 27
- Views
- 1K
Share: