You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Inelastic: Definition and 494 Discussions
In economics, elasticity refers to the measurement of a percentage change of one economic variable in response to a change in another.
View More On Wikipedia.org
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
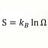
Calculate impulse force in inelastic collision
Homework Statement A bag of sand with mass=55 is dropped from h=30 ft Velocity at impact with Earth is 43.8ft/sec The impact time ( time for sand bag to come to rest) is 1/10 sec. What is the impulse force on the sand bag in this inelastic collision ?Homework Equations Impulse force = change in...- morrobay
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions in One Dimension - Need Help, due tonight
I have a lab report due tonight. We were working on these in lab and I'm not sure how to tell which one was elastic or inelastic. We had three cases. We had to use the conservation of momentum and kinetic energy formulas.A ) Cart A and B have equal masses. Car B is at rest. Car A strikes car B...- Princess19
- Thread
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Exploring Inelastic Collisions: Energy Conservation
hi, Look at this experiment http://img243.imageshack.us/img243/4150/inelasticcollision2.jpg http://img13.imageshack.us/img13/2914/inelastic2.jpg in this experiment , the law of conservation of energy can't be applied because the KE is lost but this is not true for all the cases of...- Misr
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Collisions Inelastic
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanics
-
G
Inelastic Collision with Friction and angle
Suppose the traffic investigators determined from the skid marks that these cars came to rest with a displacement of 9.72m at 72 degrees North of East, and the coefficient of friction was .72. The red car had a mass of 1000kg, but the blue car's mass was 1300 kg in this accident. Find the...- Geowarrior77
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Mechanics
-
F
Change in internal energy of an inelastic collision.
Homework Statement A car of mass 2200 kg collides with a truck of mass 4500 kg, and just after the collision the car and truck slide along, stuck together, with no rotation. The car's velocity just before the collision was < 35, 0, 0 > m/s, and the truck's velocity just before the collision...- flyboy9
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
How far does a putty block compress a spring after an inelastic collision?
Homework Statement A 0.440 kg block is attached to a horizontal spring that is at its equilibrium length, and whose force constant is 23.0 N/m. The block rests on a frictionless surface. A 5.90*10^-2 wad of puddy is thrown at the block, hitting it with a speed of 2.50 m/s and sticking. How...- jwang023
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Perpendicular Inelastic Collision
Homework Statement Two clay balls of the same mass stick together in an completely inelastic collision. Before the collision, one travels at 5.6 m/s and the other at 7.8 m/s, and their paths of motion are perpendicular. If the mass of each ball is 0.24 kg, what is the magnitude of the...- sheepcountme
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Modeling a 2-Body Collision with Simulink
Does anyone know of any inelastic impact / collision equations or theories that somehow incorporate a spring constant or Modulus of Elasticity? I have a problem where I need to show how changing a different material (ie. a different Elasticity) will affect the velocity after impact. The... -
S
Solving a 2D inelastic collision involving cars and tricycles
Homework Statement You are moving due North in your car with velocity (0, 20m/s). You see another car traveling with a relative velocity of 15 m/s with an angle of 150 degrees. You have a mass of 30 kg, the other tricyclist has a mass of 40kg and the tricycles both have mass 10kg. You...- Sally99
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Inelastic collisions and material properties
I am in the middle of a large project as an undergrad mech. engineering student and my team and I are having some modeling issues. Here is a description of our task: We must modify the design of a digital spool valve for a company. We have a spool, and 2 electro-magnetic endcaps that the... -
J
How to Calculate Kinetic Energy and Velocity in Inelastic Collisions
Homework Statement A mass weighing 1kg at the top of a frictionless hill where theta = 50 and is 3m long is released from rest and collides inelastically at bottom with a second mass weighing .25 at rest. The pair then slides up the second incline that's .5m high and fly’s off with a certain...- jamesdubya
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Collisions Inelastic
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Conservation of Momentum, a Totally Inelastic Collision
Homework Statement A 950kg compact car is moving with the velocity ⃗v1 = 32 ˆx + 17 ˆy m/s. It skids on an icy, frictionless patch and collides with a 450kg hay wagon moving with velocity ⃗v2 = 12ˆx +14ˆy m/s. If the two stay together, what is their velocity? Homework Equations...- mvl46566
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Calculating angular velocity of a ratatable bar in inelastic collision
Homework Statement 1 m long rotatable bar with a mass of 2 kg is held on vertical stick that goes through its center of gravity. A bullet with mass 0.2 kg is shot with a speed 1 m/s horizontally at the edge of the bar. After the collision the bullet lodges into the bar. Calculate the angular...- mmoadi
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Fraction of Energy Lost in Inelastic Collision | Hockey Puck Problem
Homework Statement One hockey puck of mass 0.2 kg strikes an identical stationary puck on a frictionless ice rink. If the first puck had a velocity V0 = 3.8 m/s before the collision and V1 = 0.8 m/s after in the same direction, what fraction of the energy was lost? Homework Equations...- sirfinklstin
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Inelastic Collision and Conservation of Momentum
Homework Statement A student performs a ballistic pendulum experiment using an apparatus similar to that shown it the figure. Initially the bullet is fired at the block while the block is at rest (at its lowest swingin point). After the bullet hits the block, the block rises to its highest...- mexicandeligh
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Inelastic Collision homework problem
Homework Statement Two 75.0 kg hockey players skating at 6.15 m/s collide and stick together. If the angle between their initial directions was 130°, what is their speed after the collision? (Let the motion of player 1 be in the positive x-direction and the motion of player 2 be at an angle of...- court2011
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
I
Inelastic collision and kinetic energy lost.
1. A projectile (mass = 0.17 kg) is fired at and embeds itself in a target (mass = 2.43 kg). The target (with the projectile in it) flies off after being struck. What percentage of the projectile's incident kinetic energy does the target (with the projectile in it) carry off after being struck...- IAmSparticus
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Inelastic Collisions: Solving for Spring Displacement
Homework Statement In the figure below, block 2 (mass 1.4 kg) is at rest on a frictionless surface and touching the end of an unstretched spring of spring constant 170 N/m. The other end of the spring is fixed to a wall. Block 1 (mass 2.0 kg), traveling at speed v1 = 4.0 m/s, collides with...- patelkey
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Collisions Inelastic
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Loss of momentum in supposedly isolated inelastic collsion?
I may have made a mistake in calculating, but I just finished lab homework where my calculated momentum was different before and after an inelastic collsion. Is it possible that momentum was lost in the vibration of the impact or something? The experiment placed two gliders on a level air...- bravoghost
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanics
-
J
Completely inelastic collision.
Homework Statement A wooden block and a gun are firmly fixed to opposite ends of a long glider mounted on a frictionless air track. The block and gun are a distance L apart. The system is initially at rest. The gun is fired and the bullet leaves the gun with a velocity vb and impacts the...- Jimmy25
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Perfect inelastic collision
Homework Statement Two trucks with same masses are moving toward each other along a straight line with speeds of 50 mi/hr and 60 mi/hr. What is the speed of the combined trucks after completely inelastic collision? Homework Equations P_{}1+P_{}2= (2M) V_{}f The Attempt at a Solution...- jake40208
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
W
Inelastic collision between 2 objects
Homework Statement 2 objects of equal mass collide inelastically having initial speed v. after that they move off together with speed v/3. what is the angel between the initial directions? Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution mv = 2m v/3 cos ...- wing_88
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
7
Find Initial Speed of Porsche Using Inelastic Collision
Homework Statement blah blah blah Homework Equations momentum = momentum' mv + mv = (m1+m2)v (Uk)N = friction force The Attempt at a Solution It's hard to find how to start with randomly given values. Thank you so much for your help! :D- 7skk
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Solving for initial velocity in an inelastic equation
Homework Statement A 920 kg sports car collides into the rear end of a 2300 kg SUV stopped at a red light. The bumpers lock, the brakes are locked, and the two cars skid forward 2.6 m before stopping. The police officer, knowing that the coefficient of kinetic friction between tires and road is...- tjohn101
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Z
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
Homework Statement A bullet with a mass of 3.25 g is fired horizontally at two blocks resting on a smooth and frictionless table top as shown in the Figure. The bullet passes through the first 1.25 kg block, and embeds itself in a second 1.80 kg block. Speeds v1 = 2.40 m/s and v2 = 2.60 m/s...- Zhalfirin88
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Collisions Elastic Inelastic
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Entropy change in an inelastic collision.
1. A 3 kg mass hits a stationary mass of 9 kg and sticks. What is the change in entropy? So, I figure that I will need to \DeltaS = \DeltaQ/T. However, I don't know the heat or the temperature of this reaction, so this couldn't possibly be the way to evaluate. So, I think I could...- bbhill
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Perfectly inelastic collision
Homework Statement Kevin has a mass of 84.2 kg and is skating with in-line skates. He sees his 23.2-kg younger brother up ahead standing on the sidewalk, with his back turned. Coming up from behind, he grabs his brother and rolls off at a speed of 1.74m/s. Ignoring friction, find Kevin's speed...- agadag
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Inelastic Collisions: Calculating Momentum
Homework Statement Two clay balls of the same mass stick together in an completely inelastic collision. Before the collision, one travels at 5.6 m/s and the other at 7.8 m/s, and their paths of motion are perpendicular. If the mass of each ball is 0.23 kg, what is the magnitude of the...- jmaier1
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Collisions Inelastic
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Motion of two objects in a perfectly inelastic collision
Imagine two small metal spheres of equal mass and size moving at the same speed in opposite direction collide with each other. Logically (without doing the math) it seems that both spheres will collide and just stop "dead" (because of equal mass and speed). I don't know whether I made a... -
S
Conservation of momentum in an inelastic collision
The law of conservation of momentum states that all momentum is conserved in a collision. Momentum is defined as p = mv. When a collision occurs, most of the time a lot of velocity is lost and most of the mass remains. For example, a fast moving trolley runs into a brick wall, after hitting the... -
D
Conservation of Momentum for Inelastic Collisions
Okay here goes... I'm having a hard time trying to logically understand how momentum is conserved for inelastic collisions, even though energy is lost. Since energy is lost (in the form of kinetic energy) how can the initial momentum be the same as final momentum. I know I may be confusing...- david888lee
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanics
-
C
Conservation of momentum & inelastic collisions
Homework Statement This question is related to an in-class experiment. The lab involves bouncing a ball and using a motion sensor which creates a graph representing the motion. The question is: Is the principle of conservation of momentum violated in this collision (the ball colliding with...- chelseaalyssa
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
W
What is the Initial Speed of Linked Spacecraft in an Inelastic Collision?
Question: Two spacecraft from different nations have linked in space and are coasting with their engines off, heading directly toward Mars. The spacecraft s are thrust apart by large springs. Spacecraft 1, with a mass of 1.9 x 10^4 kg, then has a velocity of 3.5 x 10^3 km/h at 5.1 degrees to...- wilson_chem90
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
What are the velocity components after an inelastic collision in 2D?
Homework Statement Two balls od the same masses collide, the first one is moving with the velocity v_1, the second is stationary. The angle between them is given by the statement: "the direction of the velocity of the first ball forms an angle \alpha=30^\circ with the plane of osculation of...- corvus606
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
Confusing Elastic and Inelastic Collisions :S
Can someone please 'stupify' the definitions of an elastic and inelastic collision? Do objects bouncing off of each other undergo elastic collisions, while objects which stick together undergo completely inelastic collisions? This concept is very confusing to me :S thank you!- rice1am
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
Dep inelastic scattering with graviton as propogater
consider deep inelastic scattering of e-p.assuming that a graviton acts as a propogater in this interaction how would it effect the structure functions of the proton.now we have a spin 2(graviton) instead of the usual spin 1(photon).basically what is the effect of this spin change on the...- raj07
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Graviton Inelastic Scattering
- Replies: 2
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
K
Coservation of momentum in inelastic collisions
If the gun club members shoot at steel targets and the bullets are traveling between 800 and 1300 fps and weigh between 112 and 220 grains how far will the fragments travel if they are less than 10 grains in size. The impact on the steel is at approximately 90 deg. So far testing has shown...- kropac1
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Collisions Inelastic Momentum
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Mechanics
-
W
Inelastic collision of snadwiches
Homework Statement On a greasy, essentially frictionless lunch counter, a submarine sandwich of mass 0.480 kg, moving with speed 3.00 m/s to the left, collides with a grilled cheese sandwich of mass 0.270 kg moving with speed 1.10 m/s to the right. 1) If the two sandwiches stick together...- weskerq8
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Angular momentum and perfectly inelastic collision
Hi, I just don't really understand rotational motion very well, and I don't know how to proceed with this problem. Homework Statement You throw a 235 g ball 26 m/s at the apparatus shown in the figure. http://volta.byu.edu/ph121/homework/hw18f3.png The apparatus catches the ball, causing it...- cozzbp
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Inelastic Momentum: Calculating Mass and Speed After Car Collision
Homework Statement A car of mass 600kg traveling at 0.8c hits another, stationary car of 800kg. The two cars stick together. What is the mass and speed of the coupled cars? Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution I found the momentum of the first car as p=gamma*mu =...- Skullmonkee
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
P
An Inelastic Collision Crash Course
1. Homework Statement Three carts move on a frictionless horizontal track with different masses and speeds. Cart 1: 4 kg (5 m/s to the right) Cart 2: 10 kg (3 m/s to the right) Cart 3: 3 kg (4 m/s to the left) Cart 1 and 2 are right behind each other on the left side of the track...- PrideofPhilly
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Inelastic Collision, only masses known
Inelastic Collision, only masses known need help Homework Statement A projectile (mass = 0.28 kg) is fired at and embeds itself in a target (mass = 2.35 kg). The target (with the projectile in it) flies off after being struck. What percentage of the projectile's incident kinetic energy does...- BATBLady
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Y
Inelastic collision and Hook’s law
Homework Statement a bullet of mass 0.005kg traveling at 120m/s hits a block at rest that falls and compresses a spring (k=99n/m) to a maximum compression of 0.121m what is the mass of the block? (solve using momentum) m1=0.005kg m2=? v1=120m/s v`=? k=99n/m x=0.121m Homework Equations...- yellowmax31
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Conserving Momentum in an Inelastic Collision: Explained
Can you explain how momentum is conserved while KE isn't in an inelastic collision?? I've though about this for a while... If KE from object X is lost during the collision it means that the object will slow down. If it does, how is momentum in the system conserved? Could you explain this by... -
L
Center of Mass Movement in a perfectly inelastic collision
1. There are two 50 kg skaters in a friction-less horizontal surface. Both have velocities of |V|=10 m/s, in opossite directions (that is, skater 1's velocity is 10 m/s i, while skater 2's velocity is -10 m/s i). They both skate parallel to each other with a distance of 1,5m. Skater 1 has a...- libelec
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Conservation of momentum and loss of energy in inelastic collisions
I just learned that, in elastic collisions, the total momentum in the system is preserved while a certain amount of kinetic energy is lost. I know that kinetic is energy may be lost in the form of heat or sound. Isn't the same energy responsible for keeping the two objects in motion and... -
P
Calculating Post-Collision Speed and Initial Speed of Two Cars at Intersection
Homework Statement Two cars collide at an intersection. car A with a mass of 2000 kg is going from west to east while car B of mass 1500 kg is going from north to south at 15 m/s. As a result of collision the two cas move together as one after. The cars now move at an angle 65 degrees south of...- physicsjessic
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Inelastic
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
More inelastic problems Homework Question - How Far Do They Slide?
Homework Statement A movie stuntman (mass 81.8 kg) stands on a window ledge 7.33 m above the floor. Grabbing a rope attached to a chandelier, he swings down to grapple with the movie’s villain (mass 66.4 kg), who is standing directly under the chandelier. (Assume that the stuntman’s center...- Spraypaint
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Inelastic
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Understanding Inelastic Collisions in Helium at Room Temperature
I wonder how inelastic a collision can be? I am thinking about a gas at room temperature; for the sake of argument let it be helium, where the first excited state is well above the available collision energies. Even in a low-velocity collision, it seems there ought to be some distortion of the...- conway
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Collisions Inelastic
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
O
Physics Inelastic Collision: Initial Velocities & Kinetic Energy
Can anyone help me with a physics Inelastic Collision question: A truck mass weighing 3000kg collides into a car that is at rest weighing mass 1000kg. they stick together after the collision and the kinetic energy loss was 100kj=J. The final velocity after the collision is 15 m/s. I need to...- onecoolcat
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help