You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Nuclear: Definition and 1000 Discussions
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear decay processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as Voyager 2. Generating electricity from fusion power remains the focus of international research.
Civilian nuclear power supplied 2,586 terawatt hours (TWh) of electricity in 2019, equivalent to about 10% of global electricity generation, and was the second-largest low-carbon power source after hydroelectricity. As of January 2021, there are 442 civilian fission reactors in the world, with a combined electrical capacity of 392 gigawatt (GW). There are also 53 nuclear power reactors under construction and 98 reactors planned, with a combined capacity of 60 GW and 103 GW, respectively. The United States has the largest fleet of nuclear reactors, generating over 800 TWh zero-emissions electricity per year with an average capacity factor of 92%. Most reactors under construction are generation III reactors in Asia.
Nuclear power has one of the lowest levels of fatalities per unit of energy generated compared to other energy sources. Coal, petroleum, natural gas and hydroelectricity each have caused more fatalities per unit of energy due to air pollution and accidents. Since its commercialization in the 1970s, nuclear power has prevented about 1.84 million air pollution-related deaths and the emission of about 64 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent that would have otherwise resulted from the burning of fossil fuels.
Accidents in nuclear power plants include the Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union in 1986, the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in Japan in 2011, and the more contained Three Mile Island accident in the United States in 1979.
There is a debate about nuclear power. Proponents, such as the World Nuclear Association and Environmentalists for Nuclear Energy, contend that nuclear power is a safe, sustainable energy source that reduces carbon emissions. Nuclear power opponents, such as Greenpeace and NIRS, contend that nuclear power poses many threats to people and the environment.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Civilian nuclear power supplied 2,586 terawatt hours (TWh) of electricity in 2019, equivalent to about 10% of global electricity generation, and was the second-largest low-carbon power source after hydroelectricity. As of January 2021, there are 442 civilian fission reactors in the world, with a combined electrical capacity of 392 gigawatt (GW). There are also 53 nuclear power reactors under construction and 98 reactors planned, with a combined capacity of 60 GW and 103 GW, respectively. The United States has the largest fleet of nuclear reactors, generating over 800 TWh zero-emissions electricity per year with an average capacity factor of 92%. Most reactors under construction are generation III reactors in Asia.
Nuclear power has one of the lowest levels of fatalities per unit of energy generated compared to other energy sources. Coal, petroleum, natural gas and hydroelectricity each have caused more fatalities per unit of energy due to air pollution and accidents. Since its commercialization in the 1970s, nuclear power has prevented about 1.84 million air pollution-related deaths and the emission of about 64 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent that would have otherwise resulted from the burning of fossil fuels.
Accidents in nuclear power plants include the Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union in 1986, the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in Japan in 2011, and the more contained Three Mile Island accident in the United States in 1979.
There is a debate about nuclear power. Proponents, such as the World Nuclear Association and Environmentalists for Nuclear Energy, contend that nuclear power is a safe, sustainable energy source that reduces carbon emissions. Nuclear power opponents, such as Greenpeace and NIRS, contend that nuclear power poses many threats to people and the environment.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 25: Alpha decay (Part 2)
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 26: Beta decay -(Part 1)
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-
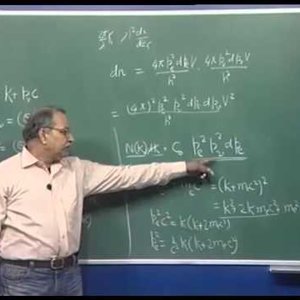
Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 27: Beta decay (Part 2)
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 28: Beta decay (Part 3)
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 29: Gamma decay
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 30: Nuclear Reactions (Part 1)
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-
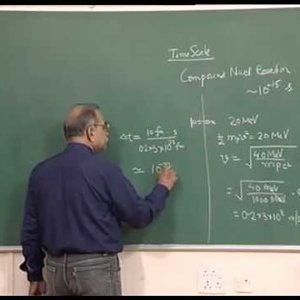
Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 31: Nuclear reaction(Part 2)
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-
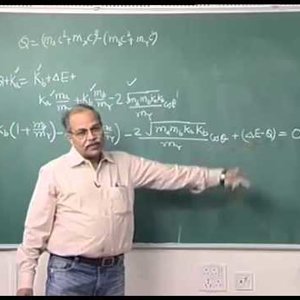
Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 32: Nuclear reaction (Part 3)
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-
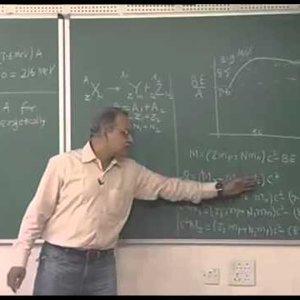
Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 33: Nuclear Fission basics
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 34: Nuclear fission of uranium
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 35: Nuclear Fission Reactor
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-
Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 36: Nuclear Energy Programme of India
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-
Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 37: Nuclear Fusion (Part 1)
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 38: Nuclear fusion (Part 2)
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-
Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 39: Thermonuclear fusion reactors
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 40: Fusion reactions in Stars and stellar neutrinos
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 41: Nucleosynthesis of elements in Stars
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 42: Mossbauer Spectroscopy
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-
Nuclear Physics by Prof. H. C. Verma (NPTEL):- Lecture 43: RBS, PIXE, NAA, Summary
Copyright reserved to Prof. Verma and NPTEL, Govt. of India. For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- nuclear
- Comments: 0
- Category: Nuclear
-

I Stellar Thermal Energy with no Nuclear source
Can anyone enlighten me as to why the total thermal energy of a star will increase with time if the star has no nuclear energy source?- mjda
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
T
Nuclear Stability: Z & N Combinations for A=22
Homework Statement Question: Discuss what values of Z and N might give stabilty to a nucleus with A=22 Homework Equations $$BE=a_vA-a_sA^{\frac{2}{3}}-a_c\:\frac{Z\left(Z-1\right)}{A^{\frac{1}{3}}}-a_s\frac{\:\left(A-2N\right)^2}{A}+\delta \left(A,Z\right)$$ The Attempt at a Solution For this...- Taylor_1989
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Mean value of the nuclear tensor operator
Does anyone know how can you prove that the mean value of the tensor operator S12 in all directions r is zero? S12 : http://prntscr.com/j3gn40 where s1, s2 are the spin operators of two nucleons. -

Engineering What Are the Options for Nuclear Engineers in Stagnant Markets?
I'm not sure this is the right area of the forum for this, but I've been wondering about what types of things people do with nuclear engineering degrees, especially those who graduate from universities in areas where nuclear power is stagnant or in decline. The last major growth period for...- Delta Force
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Nuclear
- Replies: 3
- Forum: STEM Career Guidance
-

Nuclear Fusion: Electron Thermal Transport Terminology
I am an undergrad physics major in my final semester currently taking Intro to Thermodynamics. As a final project, each student must choose a topic related to thermodynamics that is more advanced than what is covered in the curriculum and write a paper and present our findings to the class on...- Ryan Doucette
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

B How to calculate the nuclear repulsive force?
Hello! I'm wondering if there is a simple formula to calculate nuclear repulsive force at given distance between a proton and neutron? For example at 0,5 fm between them... Thank you!- Jan Nebec
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Force Nuclear Nuclear force
- Replies: 5
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-

B Where does the increase in mass come from in fission?
If energy is released during nuclear fission, why is the mass of the products (the two new nuclei and fission neutrons) greater than the mass of the original nuclei? In accordance to E=mc^2, shouldn't the release of energy result in the products having a lesser mass than the original nuclei? -
G
Working as a nuclear engineer with M.Sc. Physics
IS it possible to work as nuclear engineer or getting into nuclear industry with a M.Sc. in Nuclear Physics instead of Nuclear Engineering?- Guan
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Nuclear Engineering
-
A
B How energy is released during nuclear fission?
In a simple nuclear fission reaction an uranium atom breaks into krypton and barium releasing around 200MeV. Binding energy per nucleon (BE/A) of uranium = 7.6 MeV And binding energy per nucleon of krypton an barium is just larger than that of uranium. So in my view, around 200 MeV is used to...- aayush
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
J
I Binding Energy: Exploring How Nucleons Become Heavier
So we have a nucleus. Let's say its a helium nucleus. If I want to split this nucleus into its constituent nucleons, I must do work against the strong force which is holding it together. Now that I have done the work, the particles are no longer bound. I have done work against the strong force...- Jas
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
A What Other Phenomena Involve Nuclear Excitations Coupling with Lattice Phonons?
Mossbauer spectroscopy is an example of a nuclear (de)excitation coupling to a lattice phonons Are there any other examples of this phenomena ?- charlesmartin14
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
Q
Engineering Nuclear Engineering Jobs that Require a lot of Travel
Are there any jobs for nuclear engineering majors that require a lot of travel. International would be preferred. I would just hate to stay in one spot! Any job ideas would help!- questionmenow
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: STEM Career Guidance
-
Y
Nuclear fuel cycle boc eoc boec eoec?
Hello everyone! I have my first question in physics forum... When I read some reports I found those terms that can not be understood... 'BOC', 'EOC', 'BOEC', 'EOEC'... BOC and EOC are used frequently and I know those terms shortly but not exactly... but I can understand boec and eoec and...- Yoo Heesang
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Cycle Fuel Nuclear Nuclear fuel
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Nuclear Engineering
-
B
Thermal Neutron Absorption Rate in Water?
Homework Statement "The 2200 m/s flux in an ordinary water reactor is 1.5*10^13 neutrons/cm^2*s. At what rate are the thermal neutrons absorbed by the water?" Homework Equations (unsure) The Attempt at a Solution I know that absorption of a thermal neutron (a neutron in thermal equilibrium)...- bran_1
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Finding the magnetization in nuclear magnetic resonance
Homework Statement J-coupling term between two spins is HJ = ħJ/4 σz(1) σz(2) In the measured magnetization spectrum of the spins, this leads to the splitting of the individual spin lines by frequency J, which we’ll now derive. We can write the magnetization of spin 1 as: <M1(t)> =... -
F
Physics Which is the job of a physicist in a nuclear central?
Hi everyone! I'm near to get a physics degree. Always like me nuclear physics, how can energy be obtained by a little cuantity of matter... I want to ask you,if you know, which is the work/tasks of a physicist in a nuclear central (if they can work there :) ). I would like to be more...- Frank93
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Job Nuclear Nuclear fuel Physicist
- Replies: 6
- Forum: STEM Career Guidance
-

I Energy efficiency of nuclear and fossil fuel
Can anyone give a percentage comparision of efficiency of energy conversion in nuclear fuel and fossil fuels like oil and coal?- Ranku
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-

Is anything being done to reclassify nuclear as 'renewable'?
Here's a simple article that presents the case that nuclear is actually a renewable resource. An excerpt: Any thoughts on the matter? Do other countries consider nuclear as renewable? Japan only comes to my mind.- Posty McPostface
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: General Discussion
-
B
Comp Sci [C++] Schrodinger equation solver and nuclear density
Hi everybody! I need to compute a C++ program for solve Schrodinger equation and calculate nuclear density. My nucleus is made up of only neutrons immersed in a potential of a harmonic oscillator. Schrodinger equation is: $$[-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\triangledown^2+V_{HO}(r)]\psi=E\psi$$ with...- BRN
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-

Nuclear physics interesting experiments and activities
Hi there, I'm looking for some interesting activities regarding nuclear physics in high school. I already have: - building a cloud chamber with dry ice or peltier modules - simulating radioactive decay with dice - simulating Rutherford's experiment hitting with glass marbles a hidden target...- tinocasals
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: STEM Educators and Teaching
-
B
Nuclear physics senior project
What are some good ideas for a senior project in nuclear physics? So far I've taken the following courses (important ones): Analytical Mechanics, E&M, Introduction to Modern physics, Introduction to Nuclear physics. Right now I'm enrolled in the QM course (as well as others). I should be...- BH Wiz
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: STEM Academic Advising
-

Smallest Possible Nuclear Reactor?
What's the smallest nuclear reactor possible in terms of size and/or weight? What kind of power output could it achieve?- Delta Force
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Nuclear Engineering
-
M
Engineering What can a nuclear engineer do in a particle accelerator ?
Do they need a nuclear engineer in a Synchrotron ? if yes what kind of job does he do ?- madhisoka
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: STEM Career Guidance
-

B Nuclear Fusion energy questions
Hi guys, I have been reading about nuclear fusion and I have some doubts that I did not find the answer. I understand that the reactants are in a more energetic state than the products when the energy release occurs, however: *What triggers the release of energy? *Where does the released energy...- Arthur Rocha
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
D
Nuclear Reactor Rod Replacement Time
If an enemy had a secret nuclear reactor and they were retrieving the rods, or whatever it is that they retrieve to make secret nuclear bombs, how much time (how fast) would it take for them to retrieve their needed material? Would just a part of the reactor be shut down, and if so, what...- David Berger
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Nuclear Engineering
-

A Nuclear spin of Fluorine 19
Can anyone explain to me why angular momentum of F-19 equals to J=1/2, but if we calculate J with the shell model the result is J=5/2. Thank you- Nouki
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
H
I Is the strong nuclear force stronger than the weak force?
I've heard that the weak nuclear force is stronger than the electromagnetic force at distances of 10^-18 m. I've also heard that the strong force becomes repulsive at a distance of 0.7 fm. So if two quarks got to a distance of <<10^-18 m which force would win, the strong force or the weak force?- Hami Hashmi
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-

What is the size of the nuclear reactor part of a nuclear power plant
Good morning at all, I have to do one research of the transport of large nuclear reactors, and I need to have an idea of which is the DIAMETER, HEIGHT and WEIGHT of the reactor I think that there are a lot of different dimension, but i want to know only approximately, because i don't have...- Fabio Pastorino
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Nuclear Engineering
-
A
I Why do nuclear mass tables usually start with ....?
Why do nuclear mass tables usually start with atomic numbers larger than 8? for example see following article: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.adt.2017.05.001- alizade
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
J
B Question about the Nuclear Strong Force
Hi, Please could someone explain the differences between the strong interaction (force that hold nucleons together) and the strong force (force that holds quarks together) in terms of the exchange particles. I have been reading several online sources and there seems to be some disagreement...- Jimmy87
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Force Nuclear Strong force
- Replies: 10
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
T
Climate 300 years after nuclear apocalypse?
So, I'm writing something taking place a few centuries after a global nuclear war, but I'm unsure what the climate would be like, both in general and in the story's specific setting - the western coast of Canada. Would the average temperature or amount of yearly rainfall change? Would areas...- ToBoldlyKnow
- Thread
-
- Tags
- apocalypse Climate Nuclear Years
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Sci-Fi Writing and World Building