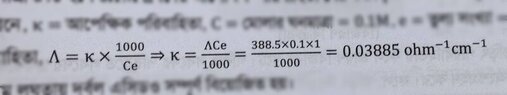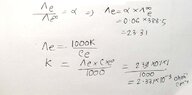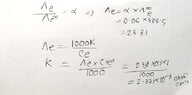- #1
nafisanazlee
- 14
- 1
- Homework Statement
- The equivalent conductance of weak monobasic acid at infinite dilution is 388.5 ohm^-¹ cm² equiv-¹ at 25 %C. Find the specific conductance of 0.1 molar solutions. the degree of dissociation of which is 6%.
- Relevant Equations
- Λe/Λe∞ = α
My attempt is the handwritten one. But my reference book solved it in a different way, they left a note saying at infinite dilution α = 1(100%). (the attached picture) Which one is the correct approach?
Attachments
Last edited: