- #1
Kaneki123
- 120
- 3
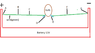
Okay...I got a question. Charges move in a wire due to an electric field across its ends. Now, positive test charge in an electric field would have higher electric potential nearer to the positive plate than anywhere else. Now in case of a circuit, like the one I have drawn, the electric potential at any point between A to D is the same (please point out if there is something wrong in the statement. My question is the, as we move further away from the positve terminal, the electric potential should decrease, so why does it not??...If someone could point out potential differences at the different points in the circuit, that'd be helpful...Any help is appreciated