- #1
Jenny Physics
- 111
- 4
Homework Statement
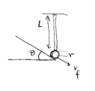
A disk of radius ##r## and mass ##m## rolls down an inclined plan. It reaches the end of the plane with velocity ##v_{f}## and collides with a vertical rod of length ##L## and mass ##M## sticking with it. See figure.
What is the angular momentum magnitude and direction after the collision?
Homework Equations
$$L=I_{disk}\omega$$
The Attempt at a Solution
The moment of inertia of the disk relative to the pivot is (using the parallel axis theorem)
$$I_{disk}=\frac{1}{2}mr^{2}+m(L+r)^{2}$$.
Angular momentum is conserved. The initial (and hence the final i.e. right after the collision) angular momentum is
$$L_{initial}=I_{disk}\omega=I_{disk}\frac{v_{f}\cos\theta}{L+r}=m\left[\frac{1}{2}mr^{2}+m(L+r)^{2}\right]\frac{v_{f}\cos\theta}{L+r}$$
Angular momentum points out of the plane since rotation is counterclockwise
However the solution is different . Where am I wrong?