- #1
ally34
- 8
- 0
Homework Statement
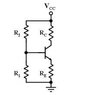
Find IB, IC, IE, VCE, VBC, and VEB for the NPN transistor in the circuit below for β = 50, 150, 500. Let VCC = 10 V, R1 = 100 KΩ, R2 = 400 KΩ, RC=2 KΩ, and RE = 0 Ω. Assume VBE = 0.7V.
Homework Equations
V = iR
IE = Ib + Ic
The Attempt at a Solution
My question is that if RE = 0 ohms, then is Ie automatically 0 amps?
But the how does Ie = Ib + Ic apply? Because I got 92.25uA for Ib and 4.56mA for Ic?
Help! :]