- #1
Duckshot
- 1
- 0
Hi I am struggling to answer this question:
The input coupling circuit of the amplifier shown in the figure consist of an RC network, with R = 1 kW and C = 5mF fed by a sinusoidal voltage source of r.m.s. amplitude of 200 mV. Assuming that the input impedance of the amplifier is, at all frequencies, so much larger than 1 kW that it can be neglected, calculate the output voltage Vo at 10Hz, 100Hz and 1kHz.
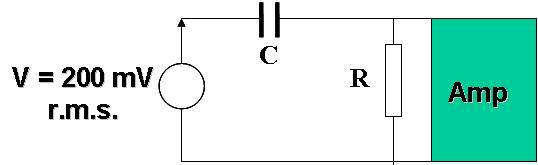
I would really appreciate any help, or if someone could point me in the right direction.
Thanks in advance
The input coupling circuit of the amplifier shown in the figure consist of an RC network, with R = 1 kW and C = 5mF fed by a sinusoidal voltage source of r.m.s. amplitude of 200 mV. Assuming that the input impedance of the amplifier is, at all frequencies, so much larger than 1 kW that it can be neglected, calculate the output voltage Vo at 10Hz, 100Hz and 1kHz.
I would really appreciate any help, or if someone could point me in the right direction.
Thanks in advance