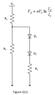
- #1
whatphysics
- 29
- 2
Homework Statement
In Figure Q22, the empirical junction diode equation is : (eqn is in the picture attached)
for both diodes D1 and D2, where VT = 26 mV at room temperature, n = 1, IS = 3.5 x 10-14 A, R1 = 600 Ω, R2 = 300 Ω, R3 = 200 Ω, VS = 9 V. Calculate the Q-points ID = _____ mA and VD = _____ V of diode D1.
Homework Equations
Shockley Diode Equation?
The Attempt at a Solution
I tried to take Id=Vs-Vd/R3 and Vd=0.026ln(Id/Is)
I would try to sub in value of Vd=0.7V into Id eqn to get Id value and then beginning the iteration process and continue this until I get a non changing Id and Vd values to 3 d.p. However, I didn't get the right answers.
Was I wrong to take R3 only for the Id equation?
The right answers are 4.18mA and 0.66V
The answers I got are way off 41.39mA and 0.72V.
Any help is greatly appreciated, thank you!