- #1
kaasisdebaas
- 4
- 0
I am looking for in an equation that's spits out the degree of polarization of reflected light, with incidence angle and the refractive indexes as inputs.
an article online article had this graph decribing the degree of polarization as a value between 0 and 1 plotted against the angle of incidence.
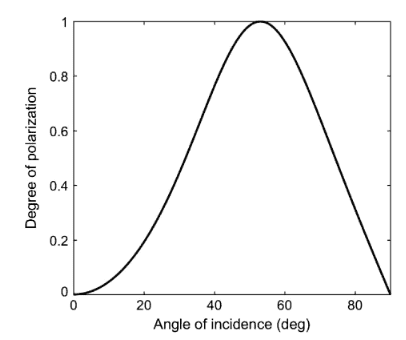
This is related to Brewsters angle, where light with an incidence angle of around 53 degrees is completely polarized when reflecting off water. my guess is that the above graph can be deduced from Fresnel/Snells equations.
Any help finding an exact equation is appreciated.
an article online article had this graph decribing the degree of polarization as a value between 0 and 1 plotted against the angle of incidence.
This is related to Brewsters angle, where light with an incidence angle of around 53 degrees is completely polarized when reflecting off water. my guess is that the above graph can be deduced from Fresnel/Snells equations.
Any help finding an exact equation is appreciated.