- #1
k.udhay
- 160
- 10
Hi,
I recently got an opportunity to work on a clutch assembly. The clutch is an old model one which has six helical springs that keep pressing the pressure plate, clutch plate and engine flywheel against each other. The cross section is:
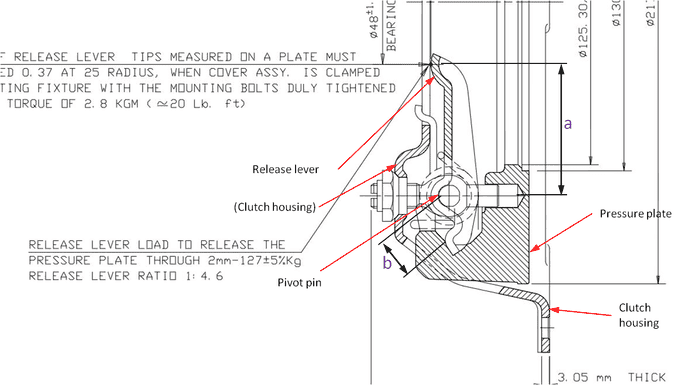
To give a brief working principle, when the release bearing presses the release lever (shown in fig.) towards right, the other end of it pulls the pressure plate on the opposite direction. The pivot is also shown in the fig. Like you can see, the lever ratio is mentioned as 1:4.6 clearly. But when I measured the dimensions 'a' and 'b' and found th ratio between them, I got a value 2.5. Can somebody explain me if there is anything wrong in what I have done pl.?
Thanks a lot.
I recently got an opportunity to work on a clutch assembly. The clutch is an old model one which has six helical springs that keep pressing the pressure plate, clutch plate and engine flywheel against each other. The cross section is:
To give a brief working principle, when the release bearing presses the release lever (shown in fig.) towards right, the other end of it pulls the pressure plate on the opposite direction. The pivot is also shown in the fig. Like you can see, the lever ratio is mentioned as 1:4.6 clearly. But when I measured the dimensions 'a' and 'b' and found th ratio between them, I got a value 2.5. Can somebody explain me if there is anything wrong in what I have done pl.?
Thanks a lot.