- #1
NowsTheTime
- 18
- 1
Hello, everyone. This is my first post!
Center of gravity does not seem like a difficult concept to grasp, but for some reason, I find it difficult to put into words.
Would I be correct in saying: the center of gravity is a point on an object that represents the average position of an object's mass? This term also takes the distribution of mass into account, and this distinguishes it from the term: center, right?
Now. Center of pressure. I stumbled upon this concept only after doing some basic web research on rockets. Would I be correct in saying: the center of pressure is a point on an object (a rocket in this case) that represents the average position of aerodynamic drag acting on an object? Of course, taking into account variations in magnitude of aerodynamic drag on the object due to its varying shape and composition.
I came up with this definition after seeing that the center of pressure of a rocket is near the bottom but above the fins.
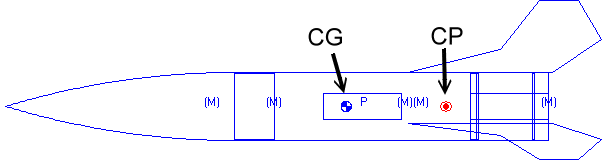
I assume that is the case because the fins induce more drag than the top of the rocket, thus skewing the average position of drag.
Thank you in advance for any responses!
Center of gravity does not seem like a difficult concept to grasp, but for some reason, I find it difficult to put into words.
Would I be correct in saying: the center of gravity is a point on an object that represents the average position of an object's mass? This term also takes the distribution of mass into account, and this distinguishes it from the term: center, right?
Now. Center of pressure. I stumbled upon this concept only after doing some basic web research on rockets. Would I be correct in saying: the center of pressure is a point on an object (a rocket in this case) that represents the average position of aerodynamic drag acting on an object? Of course, taking into account variations in magnitude of aerodynamic drag on the object due to its varying shape and composition.
I came up with this definition after seeing that the center of pressure of a rocket is near the bottom but above the fins.
I assume that is the case because the fins induce more drag than the top of the rocket, thus skewing the average position of drag.
Thank you in advance for any responses!