- #1
zeldaspurpose
- 14
- 0
Just want clarification on two equations.
So basically, I want to calculate the time period T of the complete oscillation of a cantilever. I use this equation.
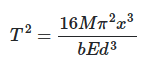
Is E equal to young's modulus or is it equal to stiffness? If it is equal to stiffness, can I use this equation to calculate the stiffness?
k =

Thank you in advance. :)
So basically, I want to calculate the time period T of the complete oscillation of a cantilever. I use this equation.
Is E equal to young's modulus or is it equal to stiffness? If it is equal to stiffness, can I use this equation to calculate the stiffness?
k =
Thank you in advance. :)