- #1
victor01
- 2
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- I have a problem getting a Clebsch–Gordan Identity
Hi, everyone. I'm trying to get the next identity
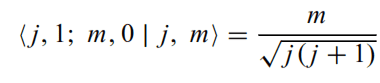
It is in the format <j1, j2; m1, m2 |j, m>. I hope you can help me
It is in the format <j1, j2; m1, m2 |j, m>. I hope you can help me