- #1
nyknicks012
- 4
- 0
Hey Guys,
I have a dynamics problem I've been working on for a few days and I'm not quite sure that the results I've gotten are correct, or even if the way I'm approaching it is.
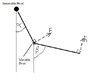
The problem consists of 2 arms connected to each other by a movable pivot. However, the whole structure cannot move translationally, and so the free end of the first arm is connected to an immovable pivot. Forces are applied at 90deg at a length lv from each arm (lv is slightly less than the total length of each arm), and friction exists at the pivot. I have attached a crude drawing of it to visualize it better. The first arm is labelled as the one connected to the immovable pivot, and all variables associated with it are denoted with a (1). The entire structure stays in the horizontal plane, and so the effects of gravity can, for the most part, be ignored.
I attempted to solve for the equations of motion using Lagrangian methods (can this even be done with applied external forces?) and I attached my attempt at a solution below. All the constants are self explanatory I'm sure, except for the coefficient of friction which is called mu.
I've taken away what I can from looking at derivations for the equations of motion for a double pendulum, but in all solutions heavy assumptions are made that make the analysis different. For example, it's assumed that the arms are massless, rigid rods with point masses at the ends, no variable forces are applied at the ends, the force of gravity is added.
Questions:
-Can the forces applied be treated as torques? It makes sense that F1 can, but not sure about F2.
-Are the frictional torque terms correct, or should they be multiplied by some length?
-Where is the axis of rotation for the second arm? Is it at the movable pivot (that's what I assumed), or is at the center of mass of the second arm?
Any help/criticism would be greatly appreciated
I have a dynamics problem I've been working on for a few days and I'm not quite sure that the results I've gotten are correct, or even if the way I'm approaching it is.
The problem consists of 2 arms connected to each other by a movable pivot. However, the whole structure cannot move translationally, and so the free end of the first arm is connected to an immovable pivot. Forces are applied at 90deg at a length lv from each arm (lv is slightly less than the total length of each arm), and friction exists at the pivot. I have attached a crude drawing of it to visualize it better. The first arm is labelled as the one connected to the immovable pivot, and all variables associated with it are denoted with a (1). The entire structure stays in the horizontal plane, and so the effects of gravity can, for the most part, be ignored.
I attempted to solve for the equations of motion using Lagrangian methods (can this even be done with applied external forces?) and I attached my attempt at a solution below. All the constants are self explanatory I'm sure, except for the coefficient of friction which is called mu.
I've taken away what I can from looking at derivations for the equations of motion for a double pendulum, but in all solutions heavy assumptions are made that make the analysis different. For example, it's assumed that the arms are massless, rigid rods with point masses at the ends, no variable forces are applied at the ends, the force of gravity is added.
Questions:
-Can the forces applied be treated as torques? It makes sense that F1 can, but not sure about F2.
-Are the frictional torque terms correct, or should they be multiplied by some length?
-Where is the axis of rotation for the second arm? Is it at the movable pivot (that's what I assumed), or is at the center of mass of the second arm?
Any help/criticism would be greatly appreciated