- #1
- 3,483
- 1,164
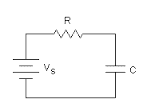
Consider the following circuit with Vs=1V,
R=1Ω and C=1F.
The voltage transfer function of the resistor can be written as
Vr(s)/Vs(s)=s/(s+1).
Now I understand s is complex frequency and at s=∞
the transfer function becomes unity since capacitor acts as a short and Vs=Vr. What I don't understand is at s=-1, the TF becomes infinity.
If s=-1 and s=σ+jω, σ=-1 gives TF=∞. What is the meaning of this? What is the general significance of σ? I know jω represents the oscillations in the system but what does the real part σ represent?
R=1Ω and C=1F.
The voltage transfer function of the resistor can be written as
Vr(s)/Vs(s)=s/(s+1).
Now I understand s is complex frequency and at s=∞
the transfer function becomes unity since capacitor acts as a short and Vs=Vr. What I don't understand is at s=-1, the TF becomes infinity.
If s=-1 and s=σ+jω, σ=-1 gives TF=∞. What is the meaning of this? What is the general significance of σ? I know jω represents the oscillations in the system but what does the real part σ represent?