- #1
James1238765
- 120
- 8
- TL;DR Summary
- What are the terms to be calculated in the "Wilson action" definition on a Yang-Mills plaquette?
The definition of the Wilson action relating to discrete Yang-Mills model is:
$$ S_{plaq} (\sigma) := \frac{1}{2}\sum_{plaq}\|I_N - \sigma_p\|^2 $$
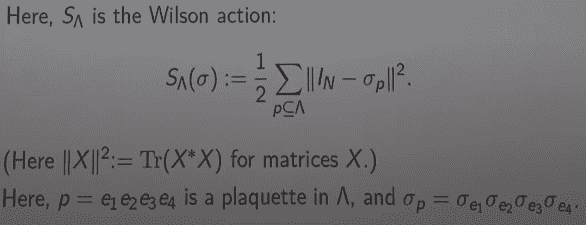
(from [here] at 5:55)
It is mentioned that ##\sigma_p## is some kind of a matrix. Could anyone give an explicit example of what a ##\sigma_p## matrix look like, please?
Does the multiplication of sigmas
$$ \sigma_p = \sigma_{e1} \sigma_{e2} \sigma_{e3} \sigma_{e4} $$
mean consecutive matrix multiplication of the four square ##\sigma_e## matrices?
$$ S_{plaq} (\sigma) := \frac{1}{2}\sum_{plaq}\|I_N - \sigma_p\|^2 $$
(from [here] at 5:55)
It is mentioned that ##\sigma_p## is some kind of a matrix. Could anyone give an explicit example of what a ##\sigma_p## matrix look like, please?
Does the multiplication of sigmas
$$ \sigma_p = \sigma_{e1} \sigma_{e2} \sigma_{e3} \sigma_{e4} $$
mean consecutive matrix multiplication of the four square ##\sigma_e## matrices?
Last edited: