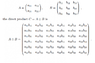- #1
Silviu
- 624
- 11
Hello! I am reading something about applications of group theory in quantum mechanics and I got confused about the difference between direct sum and direct product. In many places I found that they mean the same thing. However, the ways I found them defined in the book I read from, seem to be different, even if they use the same mathematical symbol to represent the 2 of them. I attached the 2 ways they are defined in the book. So according to these definitions, if I understand it right, If A is 2x2 and B is 3x3, the direct sum will be 5x5 and the direct product will be 6x6, which are obviously not the same thing. So, can anyone explain this to me please? Thank you!