- #1
wendys888
- 1
- 0
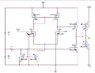
I have been experimenting with PWM circuits and I came across this CMOS comparator that seems to work well with the sawtooth generator I am using. I feed a sawtooth wave to the gate of the PMOS M3 transistor and the reference voltage I am comparing to Vin the PMOS M4.
I noticed that the PMOS's M9 and M1 are in a saturation-load NMOS setup. If I recall correctly this means they are both operating in the saturation region which generates a constant current source.
Vsaw and Vin seem to be controlling which region M3 and M4 will be operating in.
Can anyone help me in understanding the rest of this or if I completely off can someone explain to me how this is operating?
Thanks for any help!
I noticed that the PMOS's M9 and M1 are in a saturation-load NMOS setup. If I recall correctly this means they are both operating in the saturation region which generates a constant current source.
Vsaw and Vin seem to be controlling which region M3 and M4 will be operating in.
Can anyone help me in understanding the rest of this or if I completely off can someone explain to me how this is operating?
Thanks for any help!