- #1
geotechnique
- 2
- 0
Hello
Please forgive me if i am not posting in the correct forum. Also you may find my English a bit rusty since i am basically French
Ok so i want to solve some exercises in continuum mechanics . The first exercise states :
we have a stress tensor in a Cartesian coordinate system with the point O ; origin of the system , such as :
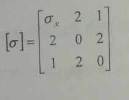
calculate σx so that one face of the stress vector is nil at point 0 ( i know it sounds odd)
Then , calculate the components of the vector n→ on this face .
Another exercise states : the function of a stress for a plain stress condition is given by :
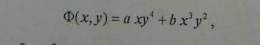
Where a and b are constants and the volume forces are ignored .
Determine the expressions of σx and σy if for the point M(1,1) the shear stress is equal to 1/2.
For the last exercise , what i have done is calculate the derivative of Φ with respect to x and did that again for y , then calculate the the two derivative functions for the point M so it gave me :
σ1 =a+3b
σ2=4a+2b
after that i applied the know functions to calculate σx and σy for a plain stress problem
it gave me these results :
σx =a+3b
σy= 4a+2b which equal exactly my first results ( not sure if this is correct tho )
Thanks
Please forgive me if i am not posting in the correct forum. Also you may find my English a bit rusty since i am basically French
Ok so i want to solve some exercises in continuum mechanics . The first exercise states :
we have a stress tensor in a Cartesian coordinate system with the point O ; origin of the system , such as :
calculate σx so that one face of the stress vector is nil at point 0 ( i know it sounds odd)
Then , calculate the components of the vector n→ on this face .
Another exercise states : the function of a stress for a plain stress condition is given by :
Where a and b are constants and the volume forces are ignored .
Determine the expressions of σx and σy if for the point M(1,1) the shear stress is equal to 1/2.
For the last exercise , what i have done is calculate the derivative of Φ with respect to x and did that again for y , then calculate the the two derivative functions for the point M so it gave me :
σ1 =a+3b
σ2=4a+2b
after that i applied the know functions to calculate σx and σy for a plain stress problem
it gave me these results :
σx =a+3b
σy= 4a+2b which equal exactly my first results ( not sure if this is correct tho )
Thanks
Last edited: