- #1
shivajikobardan
- 674
- 54
- Homework Statement
- What should I exactly write when I am asked how MPLS works?
- Relevant Equations
- None
Say there is a subject of 80 marks and I have 8-10 marks question about "How MPLS works".
I will list the information that I am planning to write(but I want your feedback on what I should write?)
What my local author textbook (that our teachers use to teach) writes-:
1) gives 1 line info about each components of mpls shim header
2) says that optimum LSP is established along with QoS parameters(2 lines).
then says
Packet enters through LERs and gets assigned a label. And it gets forwarded to LSPs. Within the domain, the LSP gets packet, remove the incoming label and attach the outgoing label and then forwards to next label switching router.
Finally the another LER strips the label reads the Ip and forwards the packet. and then normal forwarding is done.(IP forwarding).
But I feel like this is too less information for 8 marks questions. But I also feel like there is really nth more than this to explain for an undergraduate course.
These 2 topics were called "path setup" and "packet handling".
What more topics should I include in my answer? Or is this enough. I know you might say ask your teacher, this is what their slides write.
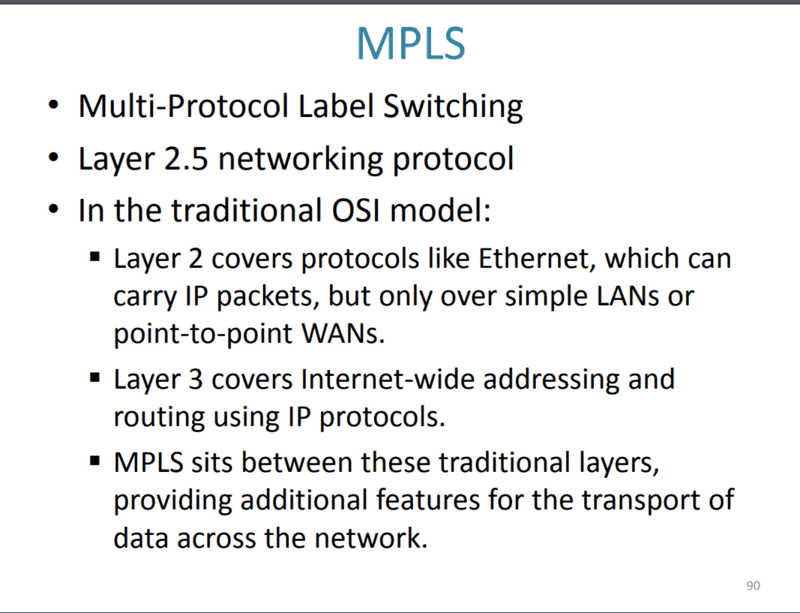
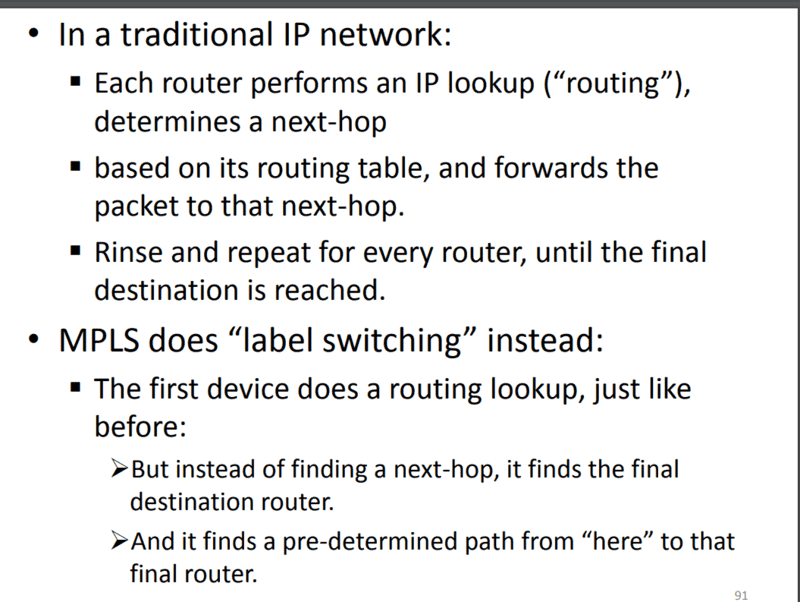
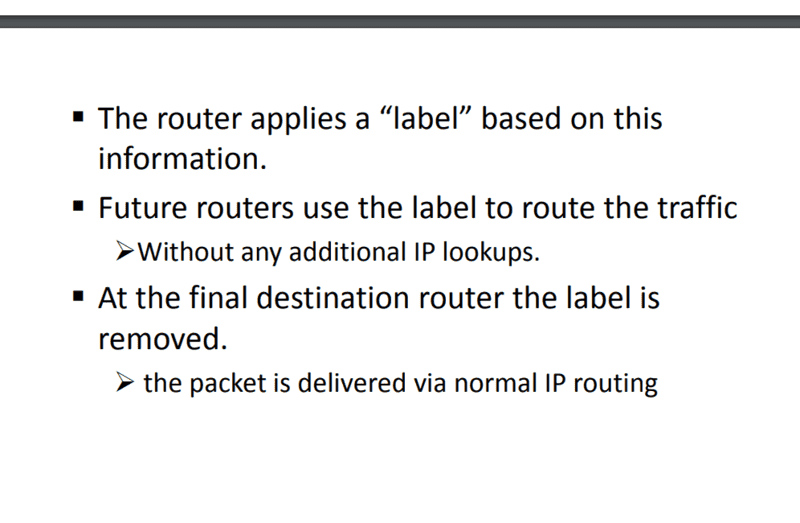
Is this information enough for 8 marks questions of UG course? Are there any details that I am missing?
What I am planning to write-:
1) mpls shim header
2) difference between conventional routing vs mpls forwarding
3) some terms related to mpls like FEC, LSP, LER,LSR, LDP (1 line definitions)
4) figure showing LER, LSR and LSP. simple one (might add LBIF as well)
5) Short explanation of how it works i.e the same thing written in slides. first comes to edge router, gets a label and based on that label gets forwarded unidirectionally and the last router pops the label and then ip forwarding starts again.
Would it be enough(not in the sense if it would be enough for my teacher..but in the sense does it really explains how mpls works?)
I am confused. It can't be this simple that you write 3 lines and you are done with the working.
I will list the information that I am planning to write(but I want your feedback on what I should write?)
What my local author textbook (that our teachers use to teach) writes-:
1) gives 1 line info about each components of mpls shim header
2) says that optimum LSP is established along with QoS parameters(2 lines).
then says
Packet enters through LERs and gets assigned a label. And it gets forwarded to LSPs. Within the domain, the LSP gets packet, remove the incoming label and attach the outgoing label and then forwards to next label switching router.
Finally the another LER strips the label reads the Ip and forwards the packet. and then normal forwarding is done.(IP forwarding).
But I feel like this is too less information for 8 marks questions. But I also feel like there is really nth more than this to explain for an undergraduate course.
These 2 topics were called "path setup" and "packet handling".
What more topics should I include in my answer? Or is this enough. I know you might say ask your teacher, this is what their slides write.
Is this information enough for 8 marks questions of UG course? Are there any details that I am missing?
What I am planning to write-:
1) mpls shim header
2) difference between conventional routing vs mpls forwarding
3) some terms related to mpls like FEC, LSP, LER,LSR, LDP (1 line definitions)
4) figure showing LER, LSR and LSP. simple one (might add LBIF as well)
5) Short explanation of how it works i.e the same thing written in slides. first comes to edge router, gets a label and based on that label gets forwarded unidirectionally and the last router pops the label and then ip forwarding starts again.
Would it be enough(not in the sense if it would be enough for my teacher..but in the sense does it really explains how mpls works?)
I am confused. It can't be this simple that you write 3 lines and you are done with the working.