- #1
cbarker1
Gold Member
MHB
- 346
- 23
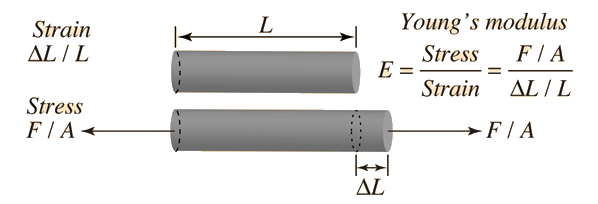
Q: Calculate the force (in N) a piano tuner applies to stretch a steel piano wire 8.50 mm, if the wire is originally 0.850 mm in diameter and 1.35 m long. (Young's modulus for steel is 20.0 ✕ 1010 Pa.)
Work F=Y*A*change in L/L_0
I have no idea what is L_0 and L_f? Please help me.
Work F=Y*A*change in L/L_0
I have no idea what is L_0 and L_f? Please help me.