- #1
melissafern
- 2
- 0
- Homework Statement
- Solve parametrically the system with g, load cell measurements and know accelerations.
- Relevant Equations
- to be found
Homework Statement: Solve parametrically the system with g, load cell measurements and know accelerations.
Homework Equations: to be found
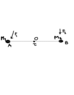
Consider that we know angles tetha(t) of a mass-less link rotating about its centerr O. - so we also have velocities and accelerations - and values of bidirectional forces on a load cell under the two masses. So we have the tengential and normal forces applied to the 2 segment extremities. I need to find the two forces vector (4 unknown) which are the 2 forces applied over the masses.
Homework Equations: to be found
Consider that we know angles tetha(t) of a mass-less link rotating about its centerr O. - so we also have velocities and accelerations - and values of bidirectional forces on a load cell under the two masses. So we have the tengential and normal forces applied to the 2 segment extremities. I need to find the two forces vector (4 unknown) which are the 2 forces applied over the masses.