- #1
sams
Gold Member
- 84
- 2
In Griffiths fourth edition, page 413, section 9.4.1. Electromagnetic Waves in Conductors, the complex wave number is given according to equation (9.124).

Calculating the real and imaginary parts of the complex wave number as in equation (9.125) lead to equations (9.126). I have done the derivation by myself and I present it here as follows:
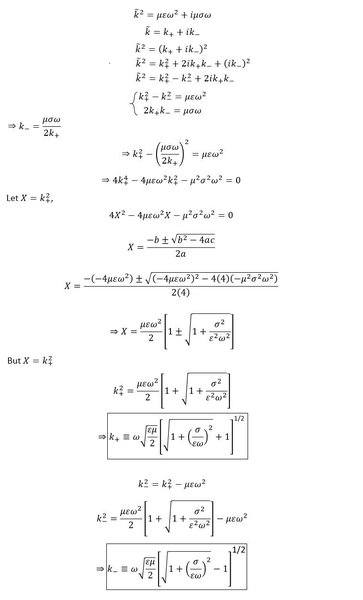
Where,
k+ is the real part of the complex wave number = k in Griffiths.
k- is the imaginary part of the complex wave number = κ (kappa) in Griffiths.
My question here is mathematical rather than physical, why did Griffiths took the positive sign of the first root of X (since X here has two roots when evaluating the polynomial of 2nd degree) when finding the real part k+ of the complex wave number?
Any help is deeply appreciated! Many Thanks!
Calculating the real and imaginary parts of the complex wave number as in equation (9.125) lead to equations (9.126). I have done the derivation by myself and I present it here as follows:
Where,
k+ is the real part of the complex wave number = k in Griffiths.
k- is the imaginary part of the complex wave number = κ (kappa) in Griffiths.
My question here is mathematical rather than physical, why did Griffiths took the positive sign of the first root of X (since X here has two roots when evaluating the polynomial of 2nd degree) when finding the real part k+ of the complex wave number?
Any help is deeply appreciated! Many Thanks!

