- #1
Bolter
- 262
- 31
- Homework Statement
- See below
- Relevant Equations
- None
Hi I made an attempt at this problem but have got the wrong answer
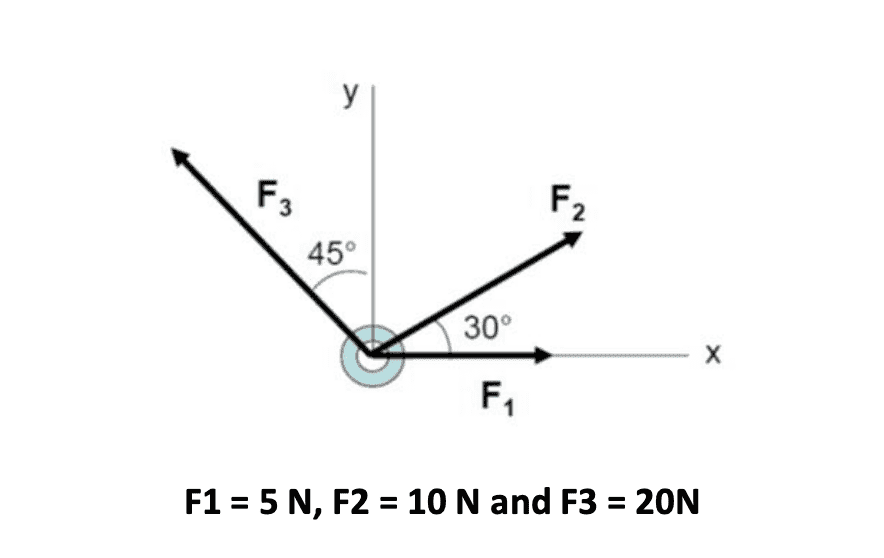

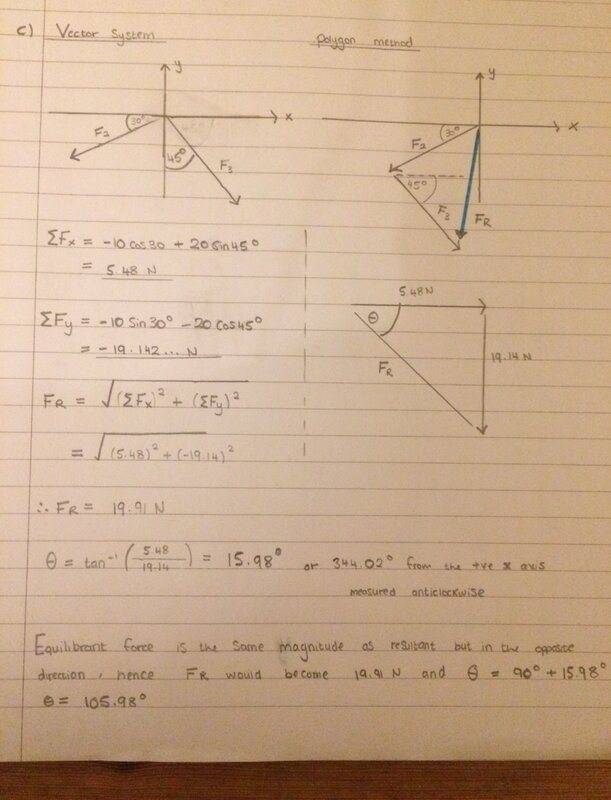
The correct answer is actually resultant force = 21.767 N at 61.34 degrees (or 151.34 degrees bearing), but I don't know how they got that?
Any help would be appreciated! Thanks
The correct answer is actually resultant force = 21.767 N at 61.34 degrees (or 151.34 degrees bearing), but I don't know how they got that?
Any help would be appreciated! Thanks