- #1
riharenda009
- 3
- 0
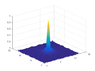
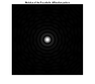
Hello, below is the screenshot from the book INTRODUCTION TO MODERN DIGITAL HOLOGRAPHY With MATLAB (TING-CHUNG POON, JUNG-PING LIU). This book is free to download. There is a script for Fraunhofer diffraction pattern and equation 1.40 is Fraunhofer diffraction formula in terms of Fourier transform.

I don't understand commands C=C*lambda*z/M/delta*1000 and R=R*lambda*z/M/delta*1000;. They are probably scaling coordinates in image plane, but I don't know how. Can anybody explain it? Thank you very much. Here are the results of the simulation. Coordinates are in milimeters.
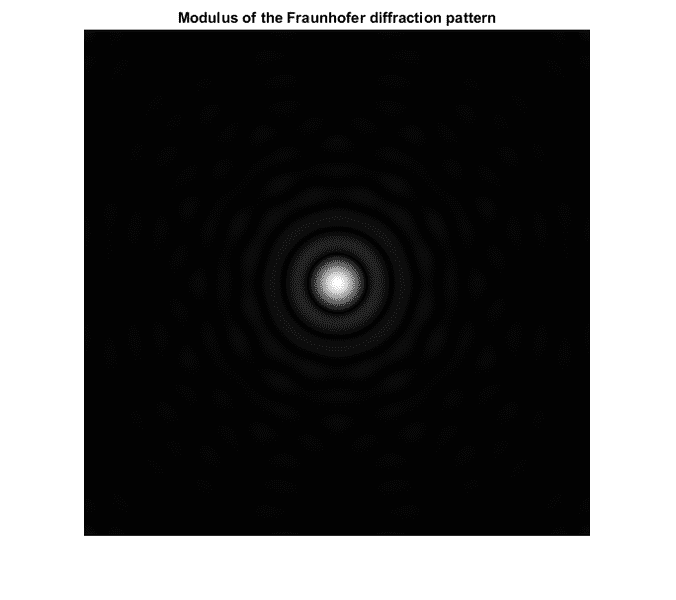
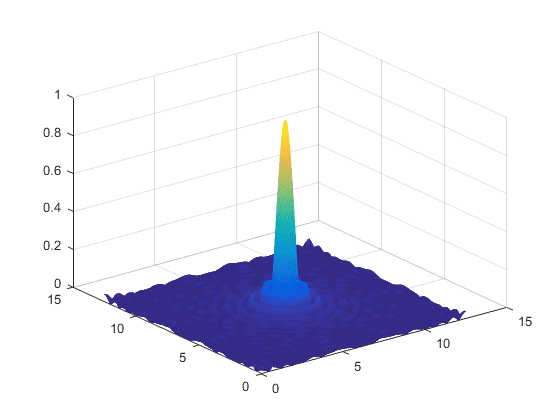

I don't understand commands C=C*lambda*z/M/delta*1000 and R=R*lambda*z/M/delta*1000;. They are probably scaling coordinates in image plane, but I don't know how. Can anybody explain it? Thank you very much. Here are the results of the simulation. Coordinates are in milimeters.