- #1
jaus tail
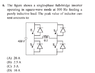
- 615
- 48
Homework Statement
Homework Equations
Fourier and then V(output) = 4Vs/(n*3.14) * sin (nwt) where Vs is battery here it's 400V
Current = V(output) / X(L). Here X is 2*3.14*100*0.2
The Attempt at a Solution
I got V(output) = 4*400/3.14 = 509.55V This is fundamental Peak output voltage.
So Current peak = 509.55 / impedance. Impedance = 2*3.14*100*0.2 = 125.6 Ohm
So Current peak = 509.55 / 125.6 = 4.06A
But this is not in option.
If i use other method of V = L di/dt
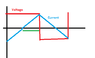
Here for time interval by green line
400 = 0.2 * di/dt
dt = time interval in green part = time period / 4. Frequency = 100 Hz. So Time period = 0.01 seconds
So dt = T/4 = 2.5 milli seconds
So 400 = 0.2 * di / dt
This gives di = 5 A.
But why don't i get correct answer if I go by above method of fourier?