- #1
mhrob24
- 53
- 9
- TL;DR Summary
- Positional tolerance for hole pattern
I have a 2 hole pattern that I’d like to control individually (meaning I don’t want them to move as a unit….I want the tolerance to be applied separately for each hole position). However, they are the same DIA, so can I just do something like this (see below)? Like, by leaving out the distance between the two holes and putting “2x” next to the tolerance box, I believe this is implying that the tolerance is separately applied to the basic dimensions constraining the holes to datum B and C. Whereas if I added the dimension for the spacing, it would imply that the holes are to be positioned as a unit (both holes can move simultaneously within the 0.25 mm tolerance zone, and the spacing would also be constrained to a 0.25mm deviation)
Is this correct? Or would I need to have a separate feature control frame for each hole?
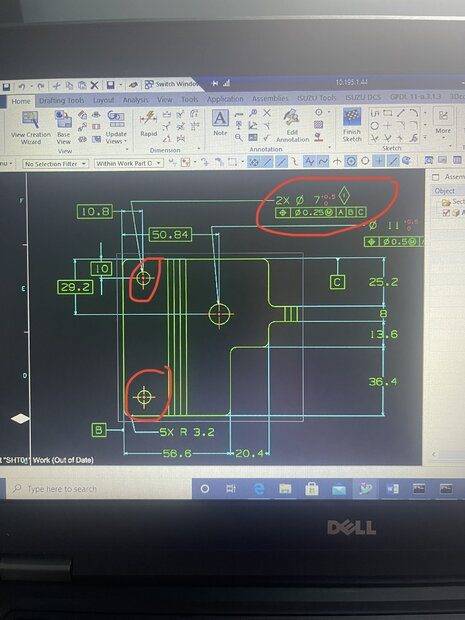
Is this correct? Or would I need to have a separate feature control frame for each hole?
Last edited: