- #1
mcfaker123
- 1
- 0
Help -- Confusion acid-base equilibrium in water
Hello,
I have been reading about the acid-base equilibrium in water. I don't understand what my book explains however. The theory may be information lacking(in my opinion). Because I've read it so many times I just decided to rewrite everything exactly from my book! I also "rewrote" 2 examples after the theory. I am also confused about what they try to accomplish in the examples. I figure they try to set up the reaction of the acid-base equilibrium in water. In the second example they marked H3O+ & OH- in red, I don't know what that means though. Then next to "simplified" they let H3O+ react with NH3. How do I know whether H3O+ reacts with NH3 or with OH-? And why is it H3O+ that reacts with NH3 and not for example Cl- that reacts with H20 or NH4+?
Im really confused with this material in my book & can't get out of it no matter what. Can anyone please help me?
Thanks in advance!
Theory:

Example 1:
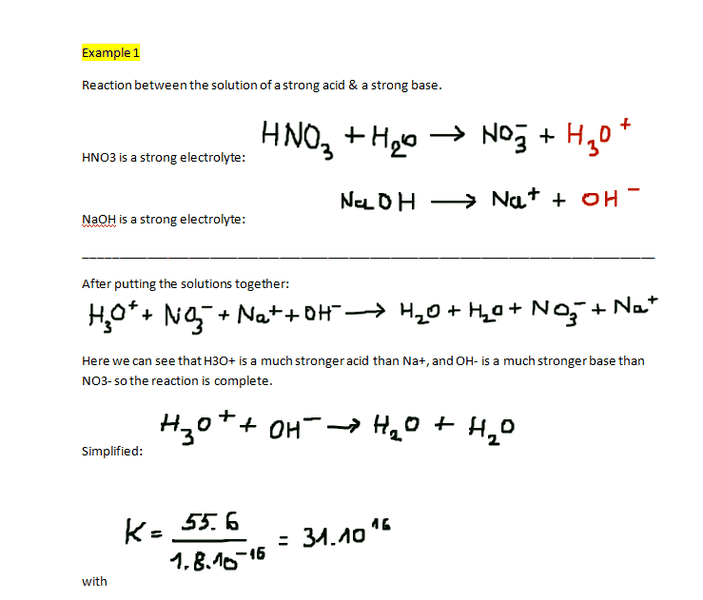
Example 2:
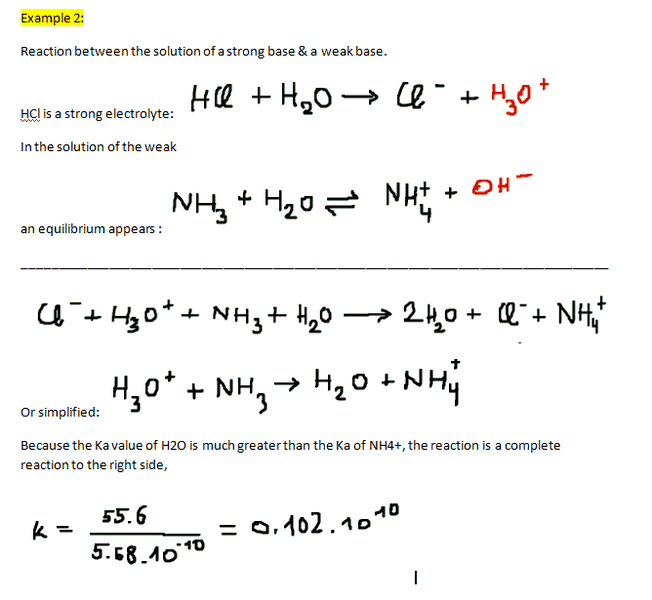
Hello,
I have been reading about the acid-base equilibrium in water. I don't understand what my book explains however. The theory may be information lacking(in my opinion). Because I've read it so many times I just decided to rewrite everything exactly from my book! I also "rewrote" 2 examples after the theory. I am also confused about what they try to accomplish in the examples. I figure they try to set up the reaction of the acid-base equilibrium in water. In the second example they marked H3O+ & OH- in red, I don't know what that means though. Then next to "simplified" they let H3O+ react with NH3. How do I know whether H3O+ reacts with NH3 or with OH-? And why is it H3O+ that reacts with NH3 and not for example Cl- that reacts with H20 or NH4+?
Im really confused with this material in my book & can't get out of it no matter what. Can anyone please help me?
Thanks in advance!
Theory:
Example 1:
Example 2: