- #1
Faye716
- 3
- 0
Hi,
I'm supposed to linearize this set of data:
"Below is a data set which includes information about the motion of the objects in the solar system. Note: the periods are listed in Earth years (time it takes the Earth to complete one orbit around the Sun) and the average distances are reported in astronomical units (1 au is a an average distance from Earth to the Sun)."
Period (yrs)
0.241
0.615
1.00
1.88
11.8
29.5
84.0
165
248
Average Distance (au)
0.39
0.72
1.00
1.52
5.20
9.54
19.18
30.06
39.44
So I plotted it, and it turned out looking like this:
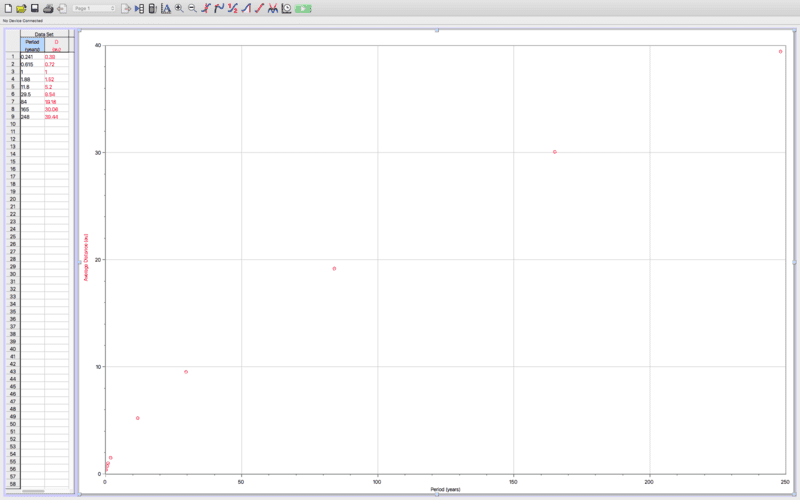
Since this looks like a square root graph to me, I took the square root of the data on the horizontal axis and plotted that. However, that ended up looking like a quadratic. In order to linearize that I would generally square the data on the horizontal axis, however that would just give me the original data again. I am stuck and do not know what to do.
After I graph and linearize it, I am supposed to "Create the mathematical model (equation) that describes the relationship between the period of an object and its average distance from the Sun. Show all work." and since I cannot linearize the data I do not know the relationship between the Period and Average distance.
Thanks in advance for the help!
Ps: Sorry if this is in the wrong forum I was not sure where to put it
I'm supposed to linearize this set of data:
"Below is a data set which includes information about the motion of the objects in the solar system. Note: the periods are listed in Earth years (time it takes the Earth to complete one orbit around the Sun) and the average distances are reported in astronomical units (1 au is a an average distance from Earth to the Sun)."
Period (yrs)
0.241
0.615
1.00
1.88
11.8
29.5
84.0
165
248
Average Distance (au)
0.39
0.72
1.00
1.52
5.20
9.54
19.18
30.06
39.44
So I plotted it, and it turned out looking like this:
Since this looks like a square root graph to me, I took the square root of the data on the horizontal axis and plotted that. However, that ended up looking like a quadratic. In order to linearize that I would generally square the data on the horizontal axis, however that would just give me the original data again. I am stuck and do not know what to do.
After I graph and linearize it, I am supposed to "Create the mathematical model (equation) that describes the relationship between the period of an object and its average distance from the Sun. Show all work." and since I cannot linearize the data I do not know the relationship between the Period and Average distance.
Thanks in advance for the help!
Ps: Sorry if this is in the wrong forum I was not sure where to put it