- #1
Abdulwahab Hajar
- 56
- 2
Hello everyone
I was hoping you could help me with something, in my analog electronics course..
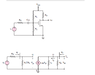
In the diagram below, is displayed a circuit and its equivalent...
I don't understand why the input resistance is only the parallel combination of R1 and R2??
Why doesn't Rsi contribute to the input resistance?
The text explains it as follows "Since the low-frequency input resistance looking into the gate of the MOSFET is essentially infinite, the input resistance is only a function of the bias resistors." but I don't get it. Maybe I wrongly understood what the input resistance is?
any explanation would be greatly appreciated
I was hoping you could help me with something, in my analog electronics course..
In the diagram below, is displayed a circuit and its equivalent...
I don't understand why the input resistance is only the parallel combination of R1 and R2??
Why doesn't Rsi contribute to the input resistance?
The text explains it as follows "Since the low-frequency input resistance looking into the gate of the MOSFET is essentially infinite, the input resistance is only a function of the bias resistors." but I don't get it. Maybe I wrongly understood what the input resistance is?
any explanation would be greatly appreciated